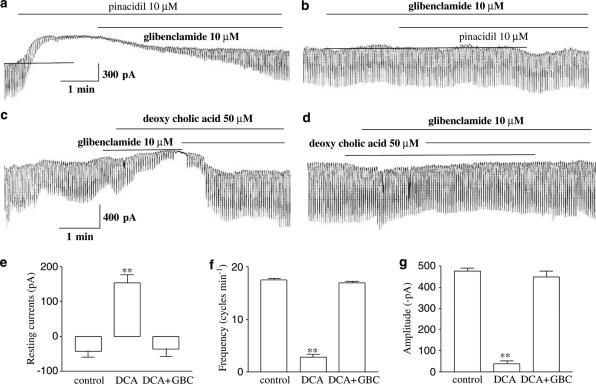
Figure 3.
Effects of pinacidil and deoxycholic acid on pacemaker currents in cultured ICC of the murine small intestine. (a) Pacemaker currents of ICC exposed to pinacidil (10 μM) at a holding potential of −70 mV. Pinacidil decreased the frequency and amplitude of the pacemaker currents, and increased the basal outward currents, and these effects were reversed by adding glibenclamide (10 μM). (b) The effects of pinacidil (10 μM) on pacemaker currents after pretreatment with glibenclamide. GBC: glibenclamide (10 μM). (c) Pacemaker currents exposed to deoxycholic acid (50 μM) at a holding potential of −70 mV. The effects of deoxycholic acid were qualitatively the same as the effects of pinacidil on pacemaker currents. Also, these effects were reversed adding glibenclamide (10 μM). (d) The effect of deoxycholic acid (10 μM) on pacemaker currents after pretreating cells with glibenclamide (10 μM). (e, f, and g) Bar graphic representation of the blocking response to glibenclamide on effects of deoxycholic acid. Bars represent mean values±s.e. **(P<0.01) Significantly different from the untreated control. The dot lines indicate the zero current levels. DCA: deoxycholic acid, GBC: glibenclamide.