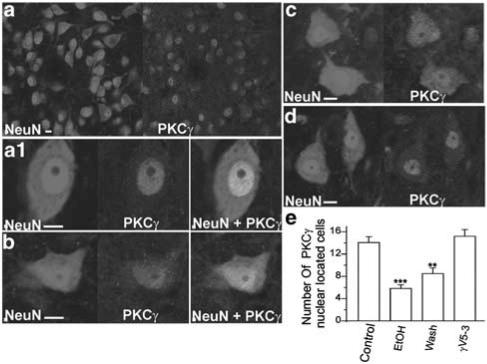
Figure 4.
Ethanol induces PKCγ translocation from the nucleus to cytoplasm. (a) Immunostaining image for spinal cord ventral horn neurons (NeuN, 1 : 750) and PKCγ isozyme (PKCγ, 1 : 500). (a1) In control conditions, the PKCγ isozyme is located in the nucleus. (b) After treatment with 100 mM ethanol for 20 min, the PKCγ translocated from the nucleus to cytoplasm. (c) After treatment with 100 mM ethanol for 20 min and wash 20 min, the majority of PKCγ staining remains in the cytoplasm. (d) Pretreatment with the PKCγ selective inhibitor, γV5-3, prevented the ethanol-induced PKCγ translocation. (e) Histogram showing ethanol-treated spinal cord ventral horn contains significantly fewer neurons with PKCγ located solely in the nucleus as compared with control (control: n=5; ethanol treated: n=5; wash: n=5; ethanol plus γV5-3 treated: n=4. n is the number of animals used; the numbers of neurons are averages of three fields per section. Two to three sections were taken randomly per animal. A total of 800–1100 neurons were analyzed for each condition.) **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. Bar=10 μm.