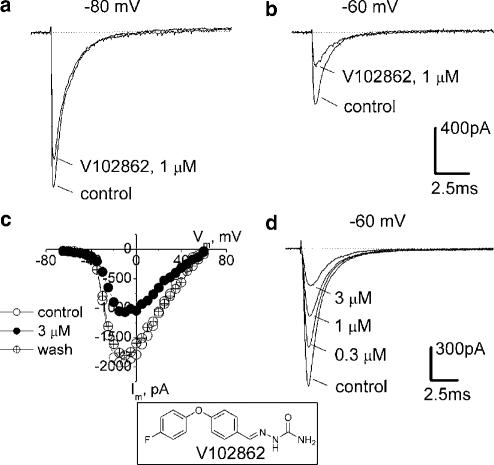
Figure 1.
Block of INa in hippocampal neurons by V102862. The currents shown in this and other figures are measured after ⩾1 min in control or drug-containing solutions, that is, under steady-state drug binding conditions. INa values were elicited by pulsing to −10 mV (maximal INa, panel c), either from holding potentials of −80 mV (a) or −60 mV (b): first under control conditions and then in the presence of 1 μM V102862 (lower and upper traces in each pair, respectively). (c) Current–voltage relationships taken in another hippocampal neuron in control, in the presence of 3 μM V102862 and upon washout. It illustrates that V102862 inhibits currents caused by different test voltages by equal amounts and does not affect appreciably the shape of current–voltage curve. Recordings were taken from a holding voltage of −70 mV by a series of test voltage pulses (25 ms long) incremented by 5 mV every other second. (d) Concentration-dependent inhibition of INa by 0.3–3 μM V102862 at −60 mV (data from a distinct neuron). Inset: The chemical structure of V102862.