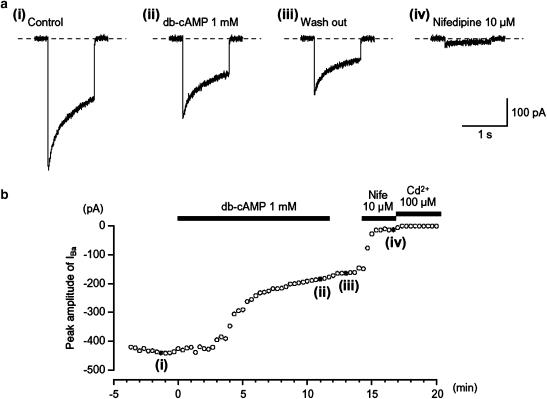
Figure 1.
Effects of db-cAMP (1 mM) on IBa using conventional whole-cell recording from an isolated gastric antral myocyte. The upper four traces show (a) inward currents, elicited by voltage steps in control solution ((a) (i)), after the application of db-cAMP ((a) (ii)), following washout of db-cAMP ((a) (iii)) and in the presence of nifedipine ((a) (iv)). The cell capacitance was 51 pF. (b) The time course of inhibition of the peak amplitude of IBa by db-cAMP (1 mM) is shown. Time 0 indicates the time when db-cAMP was applied. The inhibition produced by db-cAMP was not reversed by washing with drug-free solution. The application of 10 μM nifedipine inhibited most of the db-cAMP-resistant current. The nifedipine-resistant current was suppressed by Cd2+ (100 μM). In each experiment, inward currents were elicited by voltage steps (1 s duration) to +10 mV from a holding potential of −70 mV every 20 s.