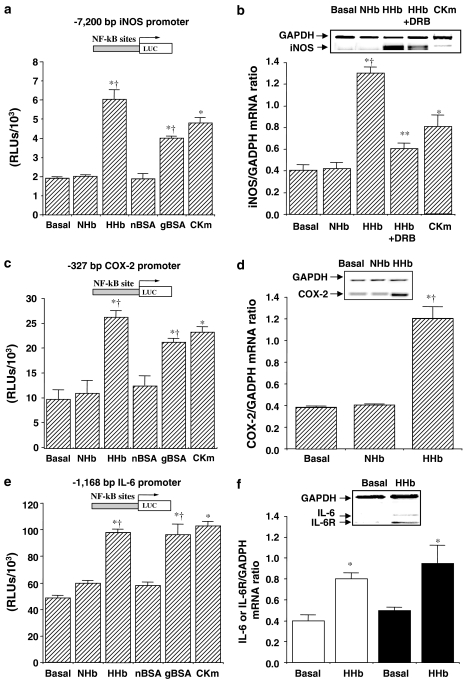
Figure 2.
Stimulation by Amadori adducts of NF-κB-related proinflammatory gene expression. The effect of Amadori adducts on either human iNOS (a), human −327/+59 COX-2 (c), and human IL-6 (e) promoters was studied using luciferase-based reporter plasmids in transiently transfected HPMCs. Cells were treated for 12 h with HHb and NHb (both at 10 nM), gBSA, and nBSA (both at 0.25 mg ml−1) or a cytokine mixture (TNF-α+IL-1β, 10 ng ml−1 each), n=32. The effect of a 6 h treatment with the above-described compounds on iNOS (b), COX-2 (d), and IL-6 (open bars) and IL-6 receptor (solid bars) (f) mRNA levels was also determined by RT–MPCR assays. Representative blots are shown, n=9. DRB: 5,6-dichloro-1-β-D-ribofuranosylbenzimidazole (10 μM). Results are expressed as mean±s.e.m. *P⩽0.05 vs basal; †P⩽0.05 vs the respective glycosylation control; **P⩽0.05 vs HHb-treated cells.