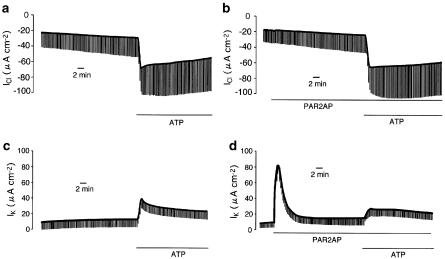
Figure 7.
(a, b) Effects of PAR2 activation on extracellular ATP-induced Cl− conductance across the apical membrane in nystatin-permeabilized Calu-3 monolayer (see Methods). To isolate apical Cl− conductance, the apical membrane Cl− current (ICl) was measured after the apical to basolateral Cl− gradient was established. An inward ICl is consistent with an absorptive Cl− flow. (a) Under this condition, Cl− conductance was continuously augmented by ATP (100 μM) added to the apical solution. (b) Even in the cells pretreated with PAR2AP (50 μM), the ATP-induced Cl− conductance was not significantly affected. (c, d) Effects of PAR2 activation on ATP-induced K+ conductance across the basolateral membrane in a nystatin-permeabilized Calu-3 monolayer (see Methods). Basolateral membrane K+ conductance was estimated through basolateral membrane K+ current after establishment of an apical-to-basolateral K+ gradient. (c) K+ conductance was increased by additon of ATP (100 μM) to the apical solution. (d) Application of PAR2AP induced a transient increase in IK. After exposure to PAR2AP (50 μM, basolateral) for 30 min, an ATP-induced increase in K+ conductance was attenuated. These experiments were performed under closed-circuit conditions.