Fig. 2.
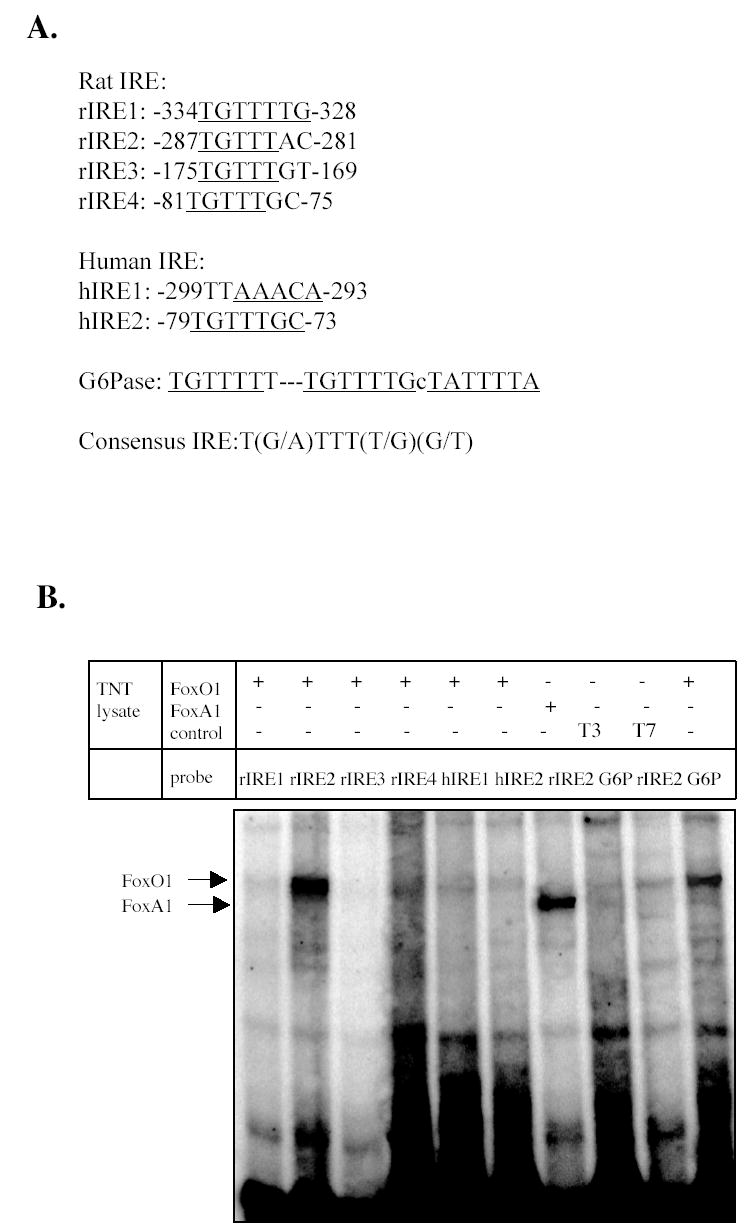

EMSA of FoxO1 and FoxA1 interaction with the putative rat and human IREs. A. Putative IREs in rat and human CYP7A1 promoter. B. EMSA of in vitro synthesized FoxO1 and FoxA1 binding to rat and human IRE probes. A G6Pase IRE probe was used as a positive control. Un-programmed TNT lysates (T3 and T7) were used as negative controls for non-specific bindings. Sequences of IRE probes used are described in Supplemental data. C. EMSA of in vitro synthesized FoxO1 and FoxA1 with 32P-labeled rat CYP7A1 IRE2 and mutant IRE2 probes. Competition assays were done with 100-fold excess of unlabeled probes. Mutation in rIRE2 probes is shown. D. Effects of FoxO1 on rat CYP7A1 reporter activities. WT: wild type rat CYP7A1 reporter (p-344/luc). IRE2 mutant: rat CYP7A1 reporter (p-344/luc) containing single nucleotide mutation in IRE2 sequence. Reporter (0.2 μg) and indicated expression plasmids (0.1 μg) were transfected into HepG2 cells. Transient transfection and luciferase assays were performed as described in Material and Methods. Mutation in rat IRE2 is shown. Statistical analysis was performed by student’s t-test, “*”, significant, P< 0.05.
