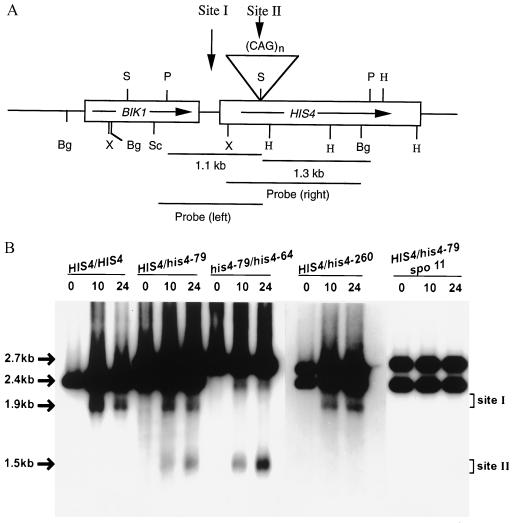
Figure 1.
Physical analysis of DSB formation in wild-type and in his4 insertion-mutant strains. (A) Partial restriction map of the HIS4-BIK1 region. The boxes indicate the coding regions and the arrows indicate the direction of transcription. All insertions were made at the SalI site within the HIS4 coding region. Abbreviations: Bg, BglII; H, HindIII; P, PvuII; S, SalI; Sc, SacI; X, XhoI. (B) DSB formation in a HIS4/HIS4 strain and in strains containing HIS4/his4-79 heterozygous or his4-79/his4-64 homozygous CAG insertions. All diploid strains were homozygous for the rad50S mutation. DNA was isolated at different times (hours) after induction of meiosis and digested with PvuII. The XhoI–BglII fragment (probe right) was used as a probe. The number above each lane indicates the time (in hours) of sample collection. Site I represents the DSB site at the HIS4 promoter. Site II indicates the DSB site at the CAG insertion. PvuII digestion of meiotic DNA generates a 2428-bp fragment for DNY115, 2428- and 2751-bp fragments (from HIS4 and his4-79 chromosome, respectively) for CJY42, and 2751- and 2706-bp fragments (from his4-79 and his4-64 chromosome, respectively) for CJY55. A similar digestion of DNY278 DNA produces 2428- and 2688-bp fragments.