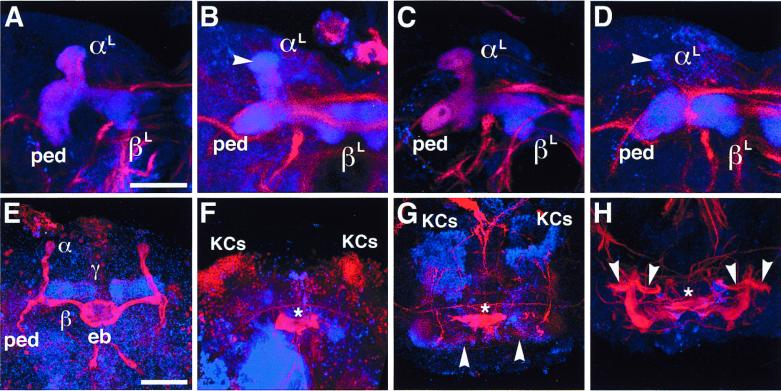
Figure 4.
Structural defects of larval and pupal MBs. Laser confocal microscopy of larval and pupal brains labeled with anti-FAS II (red) and anti-DIF (blue). (A–D) Larval MBs at the third-instar stage. (Bar = 50 μm.) (A) Wild-type MB showing peduncle (ped) and lobes (αL and βL). (B) MB in ey mutant. Note reduced and irregular FAS II expression whereas DIF staining supports structural retention of the lobes and peduncle. FAS II is lost from the globular end of the αL-lobe (arrowhead). (C) MB in dac mutant; wild-type-like MB with homogeneous and concentric FAS II and DIF staining. (D) MB in ey mutant heterozygous for dac. Note enhanced irregularity in FAS II expression and structural degeneration of the αL-lobe (arrowhead). (E–H) MBs at 50 hr after puparium formation. Neuropils were labeled with anti-FAS II (red) and anti-DIF (blue); nuclei of the Kenyon cells (KCs) were labeled with anti-EY (blue) and anti-DAC (red). (Bar = 50 μm.) (E) Wild-type MBs showing strong FAS II expression in the α- and β-lobes and DIF expression in the γ-lobe. Both FAS II and DIF were moderately expressed in the peduncles and the other lobes. eb, ellipsoid body. (F) MBs in ey mutant. All the MB structures are abolished except for Kenyon cells, which retain DAC expression (red). (G) MBs in dac mutant. Note the significant degeneration in the FAS II tracts. The lobes and peduncles are structurally irregular as revealed by weak DIF staining. Arrowheads, abnormal medial lobes. Kenyon cells expressing EY (blue) are retained. (H) MBs in dac mutant; moderate case, retaining larval-like architecture. Arrowheads indicate aberrant branching of ectopic peduncles. Stars in F–H indicate central complex remnants.