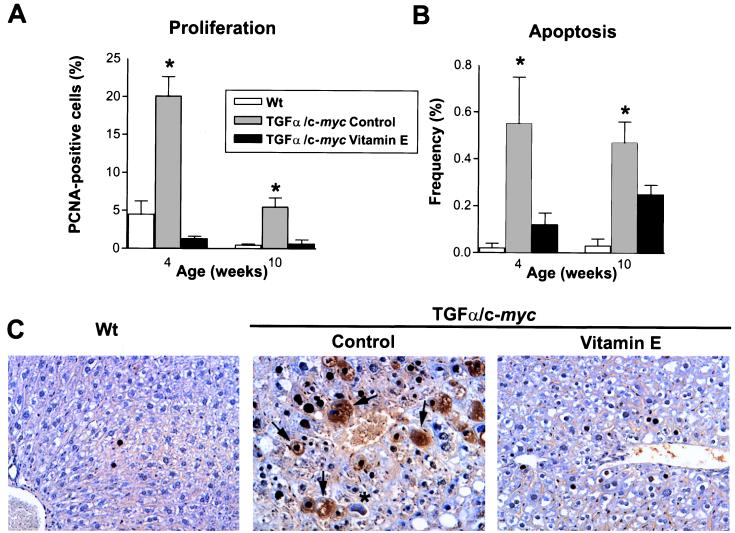
Figure 2.
VE dietary supplementation reduced the rate of hepatocyte proliferation and apoptosis in TGFα/c-myc transgenic livers. (A) Labeling index of PCNA-positive hepatocytes. Histograms show a significantly higher labeling index in TGFα/c-myc mice fed with control diet than in TGFα/c-myc mice fed with VE supplemented diet (*P = 7.1E-05 and P = 0.01 at 4 and 10 wk of age, respectively). Values are expressed as mean percentage ± SE (n = 5 in each group of mice). (B) Apoptotic index of hepatocytes. Histograms show that the apoptotic index is significantly higher in TGFα/c-myc mice fed with control diet than in TGFα/c-myc mice fed with VE supplemented diet (*P < 0.05 both at 4 and 10 wk of age). (C) Representative PCNA immunoperoxidase staining of liver samples illustrating a decreased percentage of nuclei exhibiting PCNA-immunoreactivity in 10-wk-old TGFα/c-myc mice fed with VE supplemented diet. Note the high frequency of mitotic cells (arrows) and the presence of apoptotic cells (*) in control TGFα/c-myc livers. Paraffin-embedded sections were counterstained with hematoxylin (×150 original magnification).