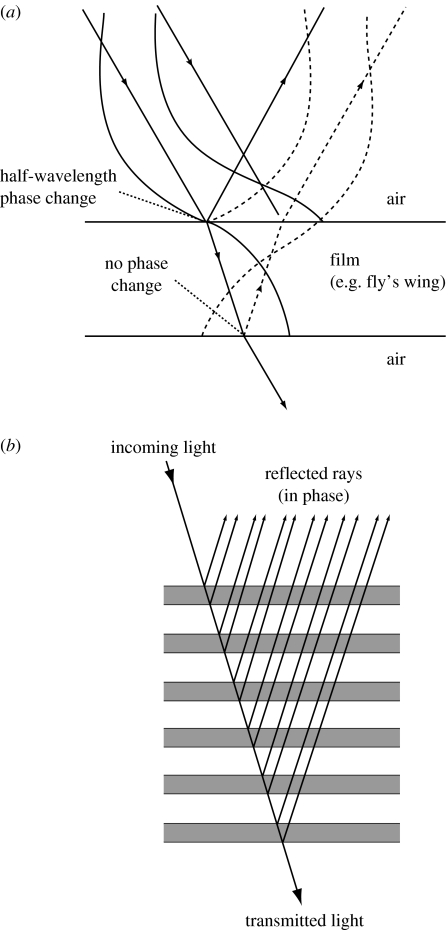
Figure 9.
(a) Light rays affected by a single thin layer, such as a fly's wing, in air. The layer is shown in cross-section; the light-ray path and wave profiles are illustrated as solid lines (incoming light) and dashed lines (reflected light). (b) A narrow-band (‘ideal’) multilayer reflector and its effect on light. Reflected rays are in phase when all the layers are approximately a quarter of their wavelength in optical thickness.