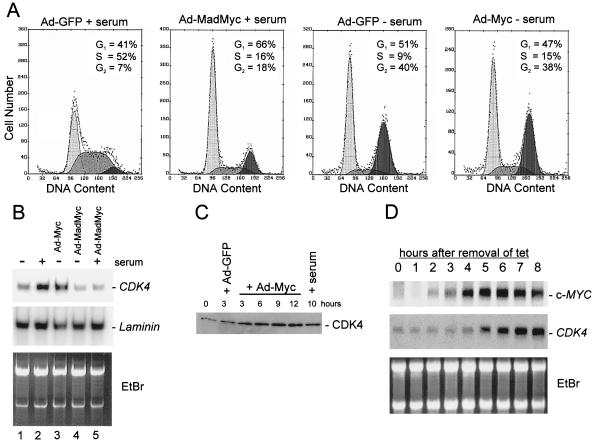
Figure 1.
Effects of ectopic c-MYC and MADMYC expression on cell-cycle distribution and CDK4 mRNA/protein levels. (A) Flow cytometric analysis of serum-starved HUVEC cells (48 h in 0.5% serum) that were infected with the indicated viruses and maintained in 0.5% serum (− serum) or restimulated by addition of 2% serum (+ serum). Cells were harvested 12 (2 left plots) or 24 h (2 right plots) after viral infection and subjected to flow cytometric analysis as described in ref. 8. (B) Northern blot analysis with RNA (2.5 μg) from HUVEC cells serum-starved (0.5%) for 24 h and then subjected to the serum stimulation (2%) and/or adenoviral infection as indicated. Membranes were hybridized with a probe for CDK4 or a control probe for laminin mRNA. (C) Western blot analysis of lysates from serum-starved HUVEC cells (48 h in 0.5% serum) infected with Ad-MYC or Ad-GFP, or serum-stimulated and harvested at the indicated times. Membranes were probed with a CDK4-specific antibody (see Materials and Methods). (D) Northern blot analysis with RNA from a human B cell line (P493–6) after activation of a conditional c-MYC allele. P493–6 cells harbor a c-MYC gene under control of a tetracycline-responsive element (24). EtBr, ethidium bromide.