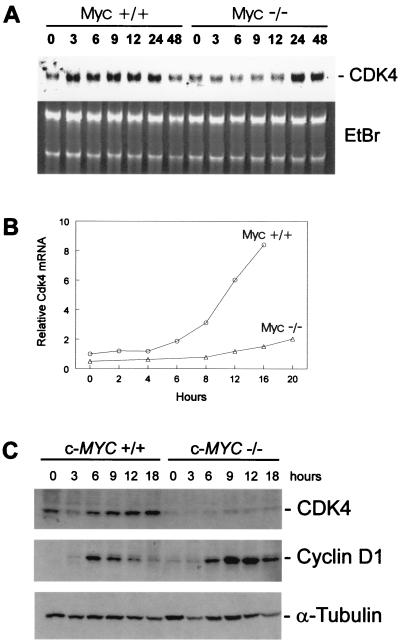
Figure 3.
Requirement of c-Myc for normal induction of Cdk4 after serum stimulation. (A) RAT1 c-Myc +/+(TGR-1) and Rat1 c-Myc −/−(HO15.19) were serum-starved for 48 h in DMEM containing 0.25% calf serum. RAT1 and RAT1 c-Myc −/− were restimulated with 10% calf serum/DMEM, and RNA lysates were prepared at the indicated times. Northern blot analysis was performed with a probe for rat Cdk4 (Upper) and total RNA was stained with ethidium bromide (Lower). (B) RAT1 c-Myc +/+(TGR-1) and Rat1 c-Myc −/−(HO15.19) were serum-starved for 48 h in DMEM containing 0.25% calf serum. RAT1 and RAT1 c-Myc −/− were restimulated with 10% calf serum/DMEM, and RNA lysates were prepared at the indicated times. Northern blot analysis was performed with a probe for rat Cdk4 and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) as an internal control. Relative Cdk4 mRNA levels were determined by quantitating the hybridization signal with a PhosphorImager (Molecular Dynamics), followed by correction for the number of cells loaded by using the internal Gapdh standards. (C) RAT1 c-Myc +/+(TGR-1) and Rat1 c-Myc −/−(HO15.19) were serum-stimulated as described in A, and protein lysates were prepared at the indicated times. Western blot analyses were performed with antibodies against CDK4, cyclin D1, and α-tubulin.