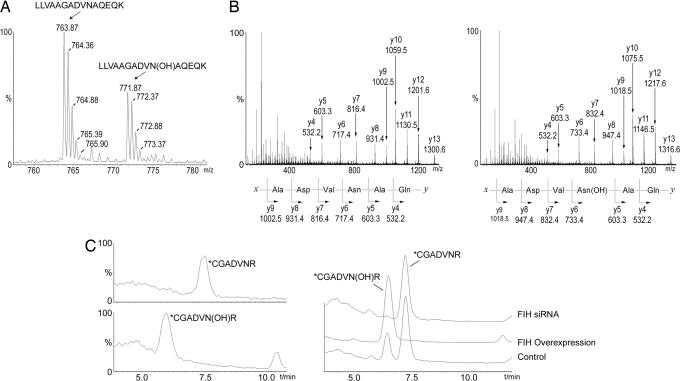
Fig. 3.
Mass spectrometric analysis of FIH-mediated hydroxylation of p105 and IκBα in vivo. (A) LC/MS spectrum from a tryptic digest of PK-tagged p105 immunopurified from transfected 293T cells. Peaks at m/z = 763.87 and 771.87 correspond to [M + 2H]2+ of unhydroxylated and hydroxylated LLVAAGADVNAQEQK peptides, respectively. Mutations (L668K/R870A) were introduced into p105 to enable LC/MS and MS/MS analysis of tryptic peptides. (B) MS/MS spectra of the m/z 763.87 (Left) and m/z 771.87 (Right) parent ions assign Asn-678 as the site of hydroxylation in p105. A +16-Da shift appears in the y-ion series appearing at y6, corresponding to fragments containing Asn-678. (C) Extracted ion chromatograms illustrating the effect of FIH intervention on IκBα hydroxylation at Asn-244. (Left) Standards for the hydroxylated and unhydroxylated modified tryptic peptides (see Fig. 9 for MS/MS assignments). (Right) Tryptic digest of HA-tagged IκBα immunopurified from transfected 293T cells; FIH overexpression increases, whereas FIH siRNA decreases, the ratio of hydroxylated to unhydroxylated peptide. (∗C indicates derivatization on cysteine; see Experimental Procedures.)