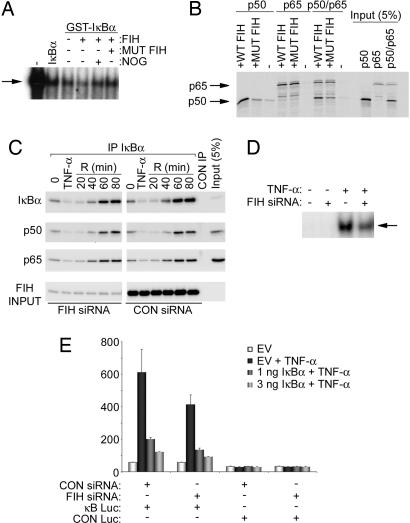
Fig. 4.
Effects of FIH on IκB/NF-κB complex formation and activity. (A) EMSA of NF-κB DNA-binding activity in nuclear extracts of TNF-α-stimulated HeLa cells. Effect of recombinant IκBα, GST-IκBα, and GST-IκBα incubated in vitro with FIH, FIH plus inhibitor (N-oxalylglycine, NOG), or mutant D201A FIH (mut FIH). Slightly more potent inhibitory effects of hydroxylated IκBα (lane 4) were consistently observed. Arrow indicates the NF-κB DNA-binding activity. IκBα inputs were normalized but not shown. (B) Interaction of recombinant GST-IκBα, pretreated with either wild type or mutant D201A FIH (mut FIH), with 35S-labeled p50 and/or p65 produced by IVTT in wheat germ lysate. Interaction was performed in the presence of BSA, assayed by GST pull-down. Coprecipitating p50 and p65 are detected by autoradiography. GST-IκBα input is normalized but not shown. (C) Association of IκBα with p65 and p50 in cells. U2OS cells were transfected with control or FIH siRNA and stimulated with TNF-α. Anti-IκBα immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with anti-IκBα, anti-p50, or anti-p65 antibodies. Cells were harvested either at time 0 (untreated), after a 30-min exposure to TNF-α (TNF-α), or at the indicated times (in minutes) after removal of TNF-α. (D) NF-κB DNA-binding activity. EMSA of nuclear extracts from serum-deprived 293T cells transfected with control (−) or FIH-specific (+) siRNA duplexes and treated with TNF-α for 30 min. Arrow indicates the NF-κB DNA-binding activity. (E) NF-κB reporter activity. 293T cells were treated with FIH or control siRNA then transfected with NF-κB (κB LUC) or control (CON LUC) reporter plasmids. Cells were stimulated with TNF-α for 6 h to induce NF-κB activity, and the ability of cotransfected IκBα to suppress reporter gene activity was assessed. Relative luciferase activity is shown as the mean ± 1 SD of triplicate samples from a representative experiment.