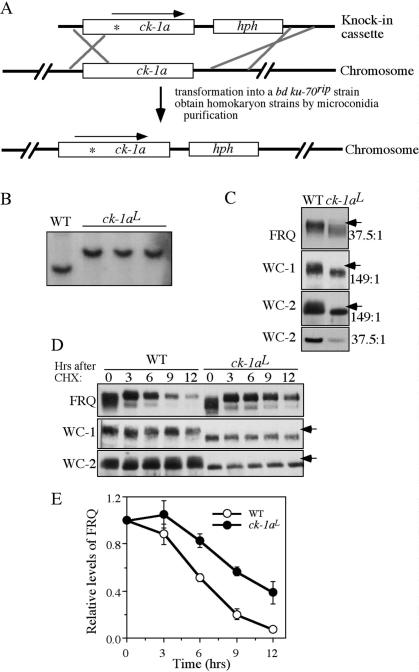
Figure 3.
FRQ, WC-1, and WC-2 are hypophosphorylated in the ck-1aL strain, a knock-in mutant carrying the dbtL mutation. (A) Graphic diagram depicting the procedures to create the homokaryotic ck-1aL strain by homologous recombination (see Materials and Methods for details). The asterisk in the ck-1a ORF indicates the location of the dbtL mutation. (B) Southern blot analysis showing the insertion of hph in the endogenous ck-1a locus. The genomic DNA was digested by SphI and the membrane was probed with a ck-1a-specific probe. (C) Western blot analyses showing that hypophosphorylation of FRQ, WC-1, and WC-2 in the ck-1aL strain. Cultures were grown in LL. The arrows indicate the extensively phosphorylated FRQ or WC species absent in the mutants. The numbers on the right indicate the ratio of acrylamide/bisacrylamide used in the SDS-PAGE. Note that for WC-2, the regular SDS-PAGE (37.5:1) failed to resolve different WC-2-phosphorylated forms. (D) Western blot analyses showing the stability of FRQ, WC-1, and WC-2 after the addition of CHX (10 μg/mL) in the wild-type and ck-1aL strains. Cultures were grown in LL. (E) Densitometric analysis from four independent experiments showing the degradation of FRQ in the wild-type and ck-1aL strains after the addition of CHX.