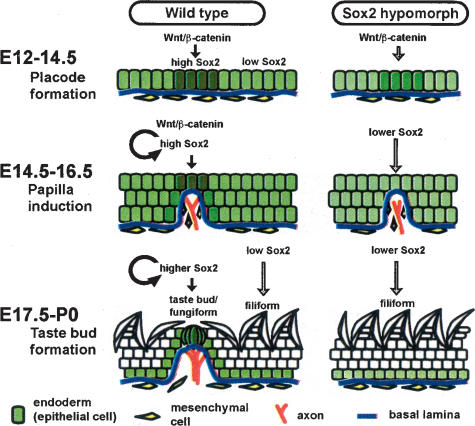
FIGURE 5.
A model for the roles of Sox2 in TB development. (Left panels) Normal development. (Right panels) Defective development in hypomorpic mutants. During placode formation stage (E12–E14), localized clusters of tongue epithelial cells express high Sox2 activated by canonical Wnt signaling. During papilla induction stage (E14–E16), the high Sox2-expressing placode cells subsequently form fungiform papillae where Wnt signaling is still active. Concomitantly there is migration of mesenchymal cells and nerves into the center of the papilla. During the TB formation stage (E17 to P0) high Sox2-expressing cells finally differentiate into TB cells, and sensory cells become innervated. In contrast, low Sox2-expressing cells normally differentiate into the keratinocytes of filiform papillae. In Sox2 hypomorphic mutants, tongue epithelial cells have lower expression of Sox2 and cannot differentiate into TB cells.