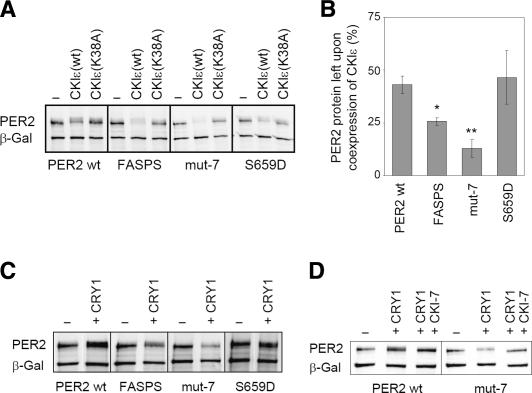
Figure 4.
The FASPS mutation leads to an increased sensitivity of PER2 toward CKIε-mediated degradation. (A) HEK293 cells coexpressing the indicated PER2 variants and either CKIε(wt) or the kinase-dead variant CKIε(K38A) were analyzed for PER2 protein abundance by Western blotting. Plasmid expressing β-galactosidase was cotransfected for normalization. (B) Quantification of the experiments described above with β-galactosidase band intensity used for normalization. The ratio between PER2 protein abundance when coexpressed with CKIε(wt) and PER2 protein abundance without coexpression of the kinase (average ± SEM, n = 2–5) is plotted. For FASPS and mut-7, the coexpression of CKIε leads to a significantly larger decrease in protein abundance than for PER2 wild type ([*] p < 0.05; [**] p < 0.01; unpaired homoscedastic t-test). (C) HEK293 cells expressing the indicated PER2 variants with or without CRY1 were analyzed for PER2 protein abundance by Western blotting. (D) HEK293 cells coexpressing CRY1 and either PER2 wild type or mut-7 were treated with the specific casein kinase I inhibitor CKI-7 or solvent. The effect on PER2 protein abundance was analyzed by Western blotting.