Figure 1.
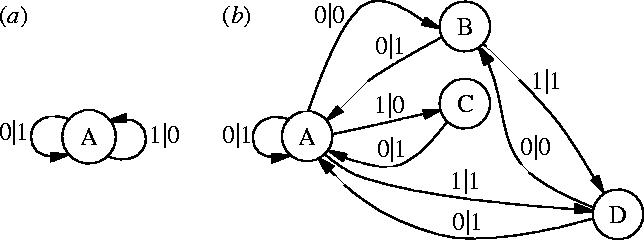
Two examples of ϵ-machines. Each consists of states (circles) and transitions (edges with labels input|output). (a) The ‘bit-flip’ ϵ-machine which, for example, takes in any binary string and produces a string of equal length in which 0s and 1s have been exchanged. It has statistical complexity zero: bits; it adds no new structure to ϵ-machines with which it interacts. (b) A typical four-state ϵ-machine found in one of the multistate finitary process soups mentioned in the text. Its statistical complexity is bits.
