Figure 1.
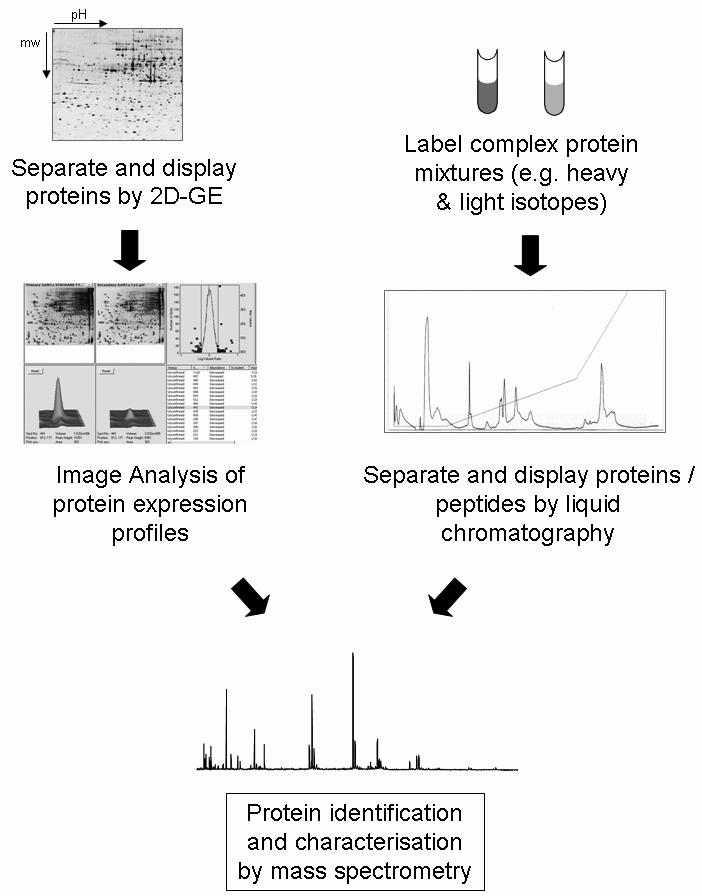
A standard proteome approach. The most common approach to separate complex protein mixtures is by 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2D-GE), which separates proteins in a pH gradient according to isoelectric point in the first dimension, and in an acrylamide matrix according to molecular weight in the second dimension. Relative levels of expression are compared between gels of different samples using computer algorithms to determine differential protein changes. Proteins of interest are excised from the gel, trypsin digested, and subjected to mass spectrometry for identification and characterisation. An alternative approach is to pre-label protein mixtures and separate proteins, or more often peptides, by multidimensional liquid chromatography. Differences in peptide levels and protein identification are then performed by mass spectrometry.
