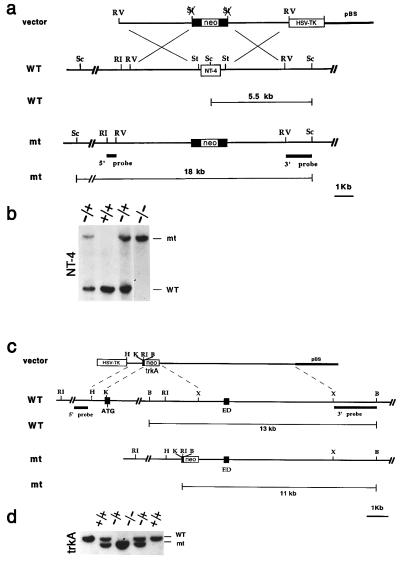
Figure 1.
Generation of NT-4 and TrkA mutant mice. (a) Schematic diagram showing the replacement vector and strategy used to inactivate the NT-4 locus. The NT-4 coding region is indicated. Restriction enzyme sites are as indicated: Sc, ScaI; RI, EcoRI; St, StuI; and RV, EcoRV. (b) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA from a litter obtained by intercrossing two NT-4 +/− mice. ScaI restriction enzyme digestion and the 3′ probe indicated in a were employed to detect rearrangement in the mouse NT-4 locus. The 5.5-kb wild-type (WT) and 18-kb rearranged (mt) DNA bands are indicated. (c) Schematic diagram showing the replacement vector and strategy used to inactivate the TrkA locus. Solid boxes indicate the TrkA exons containing the translation start site (ATG) and the extracellular domain exon (ED) corresponding to nucleotide sequence 918-1247 of the TrkA cDNA. Restriction enzyme sites are as indicated: B, BamHI; RI, EcoRI; X, XhoI; and H, HindIII. pBS indicates the pBluescript cloning vector (Stratagene). (d) Southern blot analysis of tail DNA from a litter obtained by intercrossing two TrkA +/− mice. BamHI restriction enzyme digestion and the 3′ probe indicated in a were used to detect rearrangements in the mouse TrkA locus. The 13-kb wild-type (WT) and 11-kb rearranged (mt) DNA fragments are indicated.