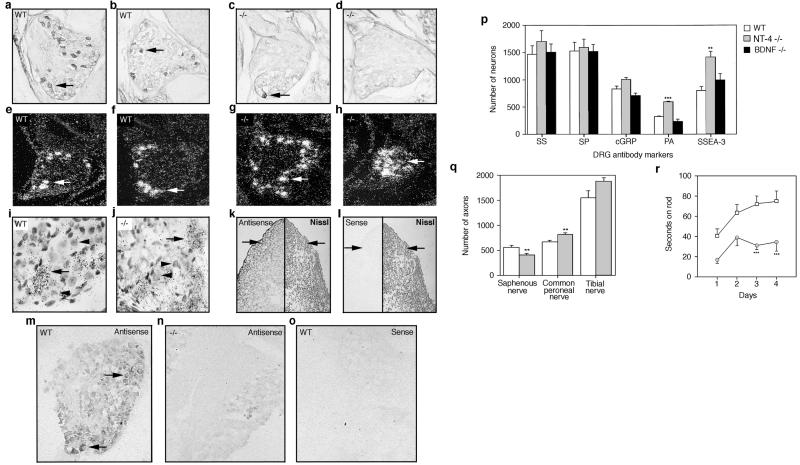
Figure 3.
Anti-TrkB antibody staining (arrows) of neonatal DRG in wt (a and b) and NT-4 mutant (c and d) mice. Dark-field view of TrkC mRNA expression in neurons (arrows) of neonatal DRG in wt (e and f) and NT-4 mutant (g and h) mice. (i and j) Higher, bright-field magnification of g and h. (i and j) Arrows indicate “positive,” TrkC-expressing neurons whereas arrowheads indicate “negative,” TrkC-expressing neurons. Digoxigenin-labeled NT-4-specific antisense and sense probes (k– o) were hybridized to E10 embryo sections of P0, wt, and NT-4 mutant DRG. (k and l) Transverse thoracic section of E10 embryo showing hybridized (Left) and Nissl-stained tissue (Right). Arrows point to region of forming DRG. NT-4 mRNA expression in neonatal wt (m and o) and NT-4 mutant (n) DRG using antisense (m and n) and sense (o) probes. (p) DRG sections from neonatal wt, NT-4, and BDNF mutant mice were immunostained with antibodies for somatostatin (SS), substance P (SP), calcitonin gene-related protein (cGRP), parvalbumin (PA), and SSEA-3. (q) Number of myelinated axons innervating cutaneous tissue (saphenous nerve) and muscle (common peroneal and tibial nerves) in wt and NT-4 mutant mice. (r) Coordination of wt and NT-4 mutant on a rotating rod over 4 consecutive days.