Fig. 2.
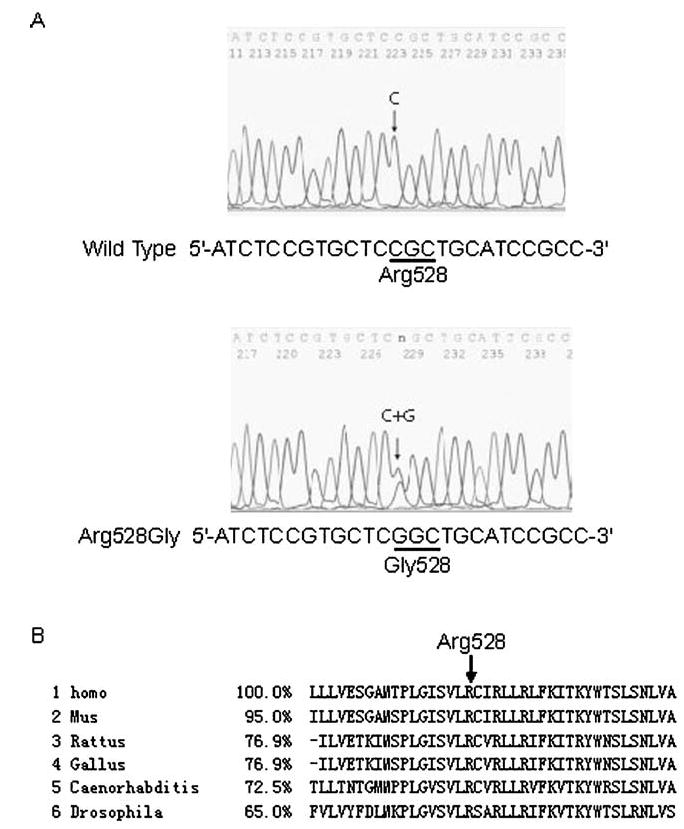
Identification of a novel mutation 1,582C →G (Arg528-Gly) of the CACNA1S gene in the Chinese family with Hy-poPP. a DNA sequences for a normal family member (wild type) and the proband III-1 (Arg528Gly) are shown. The nucleotide residue where the mutation occurs is indicated by an arrow. The C to G change at codon 528 results in the substitution of an arginine residue by a glycine residue in DIIS4 (GenBank accession NM_000069). b The alignment of amino acids around Arg528 revealed evolutionary conservation of this residue from the C. elegans and fly (Drosophila) to the humans (Homo). The percentage of identity to the human gene is shown. Homo Homo sapiens, Mus Mus musculus, Rattus Rattus norvegicus, Gallus Gallus gallus, Caenorhabditis Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila Drosophila melanogaster
