Fig. 2. The effect of missense mutations of TBX5 on DNA-binding activity.
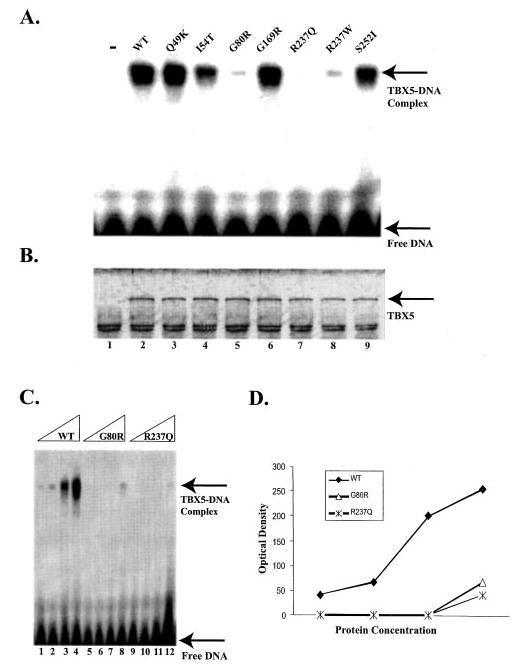
The wild type and mutant TBX5 proteins were synthesized in vitro using the TNT-coupled transcription/translation system. The TBX5-binding site is a synthetic double-stranded DNA fragment corresponding to the region from −257 to −242 bp upstream from the ANF transcriptional start site (5′-aataTCACACCTgtac-3′). A, EMSA. Lane “−,” no TBX5 protein; WT, wild type TBX5; Q49K, I54T, G80R, G169R, R237Q, R237W, and S252I, TBX5 with individual mis-sense mutations. B, a silver-stained protein gel showing the approximately equal level of synthesis of wild type and various mutant TBX5 proteins used in EMSA. Lane 1, no TBX5 expression plasmid DNA; lane 2, wild type TBX5; lanes 3–9 represent Q49K, I54T, G80R, G169R, R237Q, R237W, and S252I mutant TBX5, respectively. C, EMSA with various amounts of wild type TBX5 and mutants G80R and R237Q. D, the amount of the TBX5-DNA complex in panel C was plotted against TBX5 concentrations. The fitted slope for specific binding of wild type TBX5 (WT) and mutants G80R and R237Q is 79.5, 19.5, and 11.7, respectively.
