Fig. 3. The effect of missense mutations of TBX5 on transcription activation activity in the presence or absence of NKX2.5.
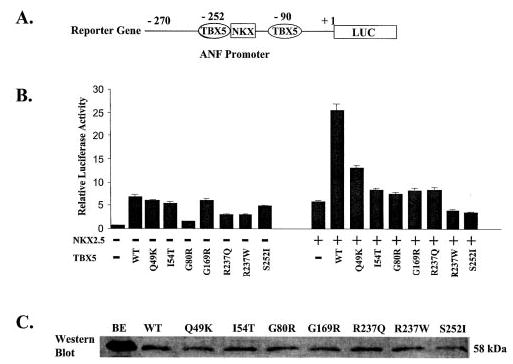
A, the reporter gene used for transcriptional activation assay. The promoter region, from −270 to +1 bp upstream from the transcriptional start site, of ANF was fused to the luciferase gene (LUC). B, transcriptional activation assay for all seven missense mutations of TBX5 in the absence (left block) and presence (right block) of NKX2.5. Transcriptional activity is shown as relative luciferase activity on the y-axis. The transcriptional activity for the vector only was set arbitrarily to 1. WT, wild type. Note that all missense mutations of TBX5 abolished synergistic transcription activation of the ANF promoter between TBX5 and NKX2.5. C, Western blot analysis to determine whether mutant TBX5 were successfully expressed in transfected COS-7 cells. BE, purified wild type TBX5 control from a bacterial over-expression system; WT, lane with lysate from COS-7 cells containing expressed FLAG-tagged wild type TBX5; Q49K, I54T, G80R, G169R, R237Q, R237W, and S252I, lanes with lysates from COS-7 cells containing expressed TBX5 proteins with corresponding mutations.
