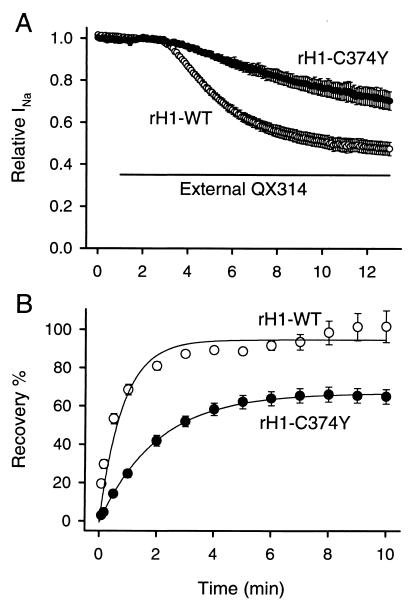
Figure 5.
Reverse mutation of rH1 to μ1 sequence (rH1-C374Y) inhibits block by external QX and slows down dissociation of internally applied QX. (A) Effects of externally applied QX314 on rH1-WT (○) and rH1-C374Y (●). The bar indicates the period during exposure to 500 μM QX314 in the bath solution. Currents were elicited by 35-ms pulses to −20 mV from a holding potential of −110 mV at 5-s intervals, and peak currents were normalized to peak current in control. Data represent the means ± SEM from seven oocytes for rH1-WT and five for rH1-C374Y. (B) Effects of rH1-C374Y on recovery from internally applied QX222 block. QX222 was internally applied by microinjecting 50 nl of a 3 mM QX222 solution into oocytes. Twenty to thirty min after microinjection, a 1-Hz train of 20 pulses with 35-ms duration was applied to −20 mV from a holding potential of −110 mV to produce use-dependent block by QX222. Then, recovery from QX222 block was monitored at the indicated intervals after the end of a train for rH1-WT (○) and rH1-C374Y (●). Peak currents during recovery were normalized by the difference between the peak current during the 1st and 20th pulses of a train, and plotted as recovery %. The smooth lines are single exponential fits, and data represent the means ± SEM from four to eight oocytes for rH1-WT and three to four for rH1-C374Y.