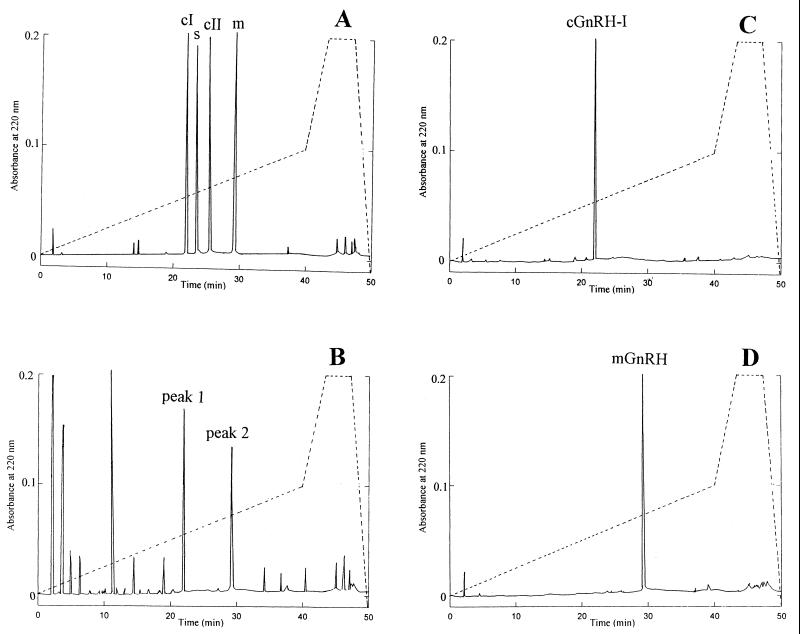
Figure 1.
RP-HPLC of synthetic and native GnRHs. (A) Elution of four synthetic GnRH molecules mixed in buffer. Dashed line represents the stepwise gradient (see Materials and Methods for details). Five micrograms of each peptide was added in combination. Peaks were identified from chromatographs of individual peptides run separately or combined under similar conditions. Elution time for chicken I (c-I), salmon (s), chicken II (c-II), and mammalian (m) GnRHs was 21.9 min, 23.5 min, 25.1 min, and 29.1 min, respectively. (B) Elution of gonadal extract from C. intestinalis after step 4 of purification (see Table 1) under similar conditions was as in A. Peaks 1 and 2 were GnRH-immunoreactive and were subjected to further purification and structural characterization. (C) Elution of purified peak 1. Note the exact correspondence of the retention time with that of synthetic cGnRH-I as in A. (D) Elution of purified peak 2. Note the correspondence of the retention time with that of synthetic mGnRH as in A. In each graph, one of several HPLC runs is shown; all column runs of each graph generated similar UV absorbance peaks.