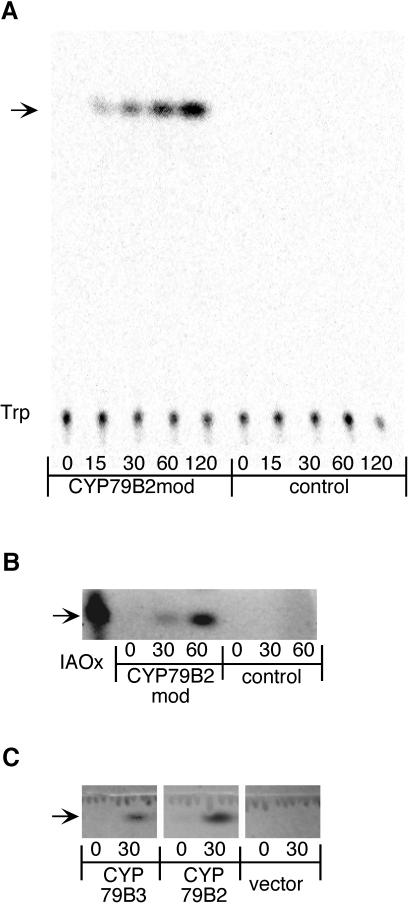
Figure 2.
CYP79B2 and CYP79B3 convert Trp to IAOx. (A) CYP79B2 metabolizes Trp. E. coli membrane extracts carrying CYP79B2mod or a non-P450 cDNA (control) were assayed for Trp-metabolizing activity as described in Materials and Methods. Radioactive compounds derived from [14C]Trp were detected by using a Bio-Rad Molecular Imager. The positions of Trp and the reaction product (arrow) are indicated. Reaction times are indicated in minutes. (B) IAOx comigrates with the CYP79B2mod reaction product. Similar samples as in A were assayed for Trp-metabolizing activity except that nonradioactive Trp was substituted for [14C]Trp. Indolic compounds were visualized by UV epifluorescence by using a Bio-Rad Fluor-S imager. Positive images were inverted into negative images by using Adobe photoshop le 3.0. Images were cropped to exclude nonessential portions. IAOx was loaded as a standard. Reaction products are indicated by an arrow, and reaction times are indicated in minutes. (C) CYP79B3 has an activity similar to CYP79B2. Membrane extracts prepared from E. coli expressing CYP79B3, CYP79B2, or the pBluescript KS(+) vector were assayed for Trp-metabolizing activity as in A, and the reactions were visualized as in B. Reaction products are indicated by an arrow, and reaction times are indicated in minutes.