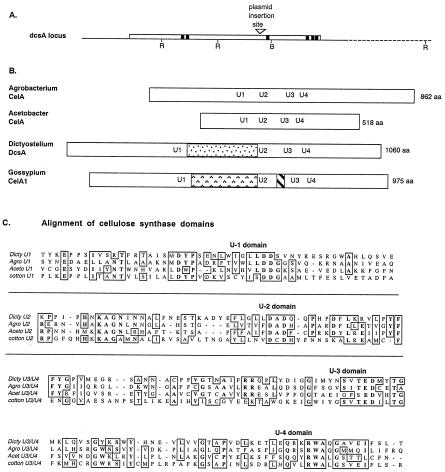
Figure 2.
Structure of the dcsA gene and comparison of its product, DcsA, with related proteins. (A) The region flanking DpnII restriction site (▿), where plasmids were found to have inserted in strains DG1099 and DG1128, contains a single, large ORF of 3.2 kb (open box). Pertinent restriction sites (RI, EcoRI; B, BglII) are marked. Sequences encoding hydrophobic domains of ≥20 aa are shown as solid boxes. (B) The predicted product, DcsA, is most similar to the cellulose synthases of A. tumefaciens and A. xylinum and could be aligned on the basis of conserved motifs U2–U4, which are marked at their position within each protein. An insertion occurred between the U1 and U2 motifs in both DcsA and the putative cellulose synthase of cotton, G. hirsutum, CelA1. However, the sequence of the insert is not conserved between these organisms. (C) Detailed comparison of the amino acid sequences surrounding the conserved motifs shows extended similarities especially between the established bacterial cellulose synthases and DcsA.