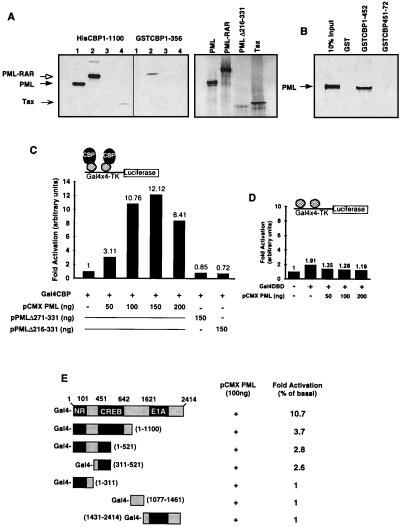
Figure 2.
PML and CBP proteins interact in vivo and in vitro. (A) In vitro association of bacterial expressed CBP and S35 radiolabeled PML wild-type and mutant PMLΔ216-331, PML-RAR, and Tax proteins. In the pull-down experiment, the loaded proteins were used at 5:1 ratio compared with the input proteins represented on the right part of the figure. All samples were analyzed in a 4–20% SDS gradient gel, as indicated. (B) In vitro mapping of the PML-CBP interaction domain. GST fusion proteins containing the indicated residues of CBP were tested for binding to radiolabeled PML. CBP451-722 contains the Tax/CREB interaction domain (i.e., amino acids 451–661). (C) PML-CBP interaction in a one-hybrid analysis. CV1 cells (48-well plates) were transiently cotransfected with 100 ng of Gal4-tk-Luc reporter construct, 90 ng of CMXβgal, 60 ng of Gal4CBP, and the expression vectors for PML wild type and mutant, as indicated, per transfection point. All of the transfection points were equalized for the total amount of expression vectors, i.e., CMX empty vector, at a 200-ng final concentration. All points were performed in triplicate and varied by <10%. The presented values correspond to a representative experiment of at least four independent assays. (D) Transfections using the Gal4 DNA-binding domain as a control. (E) Mapping the PML-CBP interaction domain in vivo. CV1 cells were transfected and analyzed as in C. Expressions vectors at 100 ng were used as indicated.