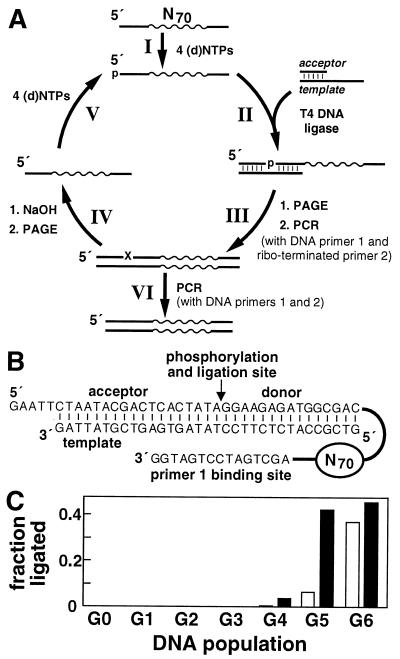
Figure 1.
Selection of self-phosphorylating deoxyribozymes. (A) Selection is initiated by incubating a population of synthetic 100-nt DNAs that carry a random-sequence domain of 70 nt. DNAs are (I) incubated with a mixture of either the four standard NTPs or the four standard dNTPs. After incubation, the DNA pool is (II) combined with excess acceptor and template oligonucleotides and treated with T4 DNA ligase in the presence of ATP. The ligated DNAs (≈123 nt) are (III) isolated by PAGE, and the recovered DNAs are selectively amplified by PCR using primer 1 and ribo-terminated primer 2. The resulting double-stranded PCR products are (IV) treated with NaOH to cleave the isolated RNA linkage, and the subsequent single-stranded DNAs are purified by PAGE and used (V) to initiate the next round. DNA populations from the final rounds of selection were (VI) PCR-amplified with primer 1 and the “all-DNA” version of primer 2 to facilitate cloning. N70 represents the random-sequence domain. (B) Sequences of the DNA population complexed with the acceptor and template strands. (C) Response of the NTP (open bars) and dNTP (filled bars) populations over the first six rounds of selection.