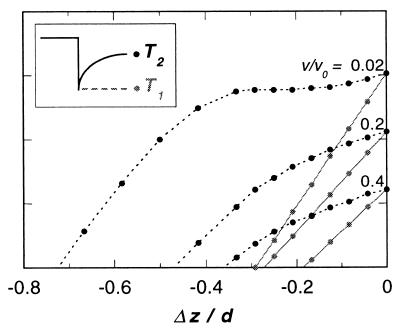
Figure 6.
Transient tension in a model fiber after a step-change in length of Δz per filament pair. The “fiber” consisted of a series of filament pairs, joined end-to-end to mimic 50 sarcomeres. Initially the fiber was contracting under load such that the average sliding velocity between filaments was v. It was assumed that the sudden step change of length caused an equal shortening of each filament pair. In response, bound heads adjusted the chemical equilibrium of the power stroke reaction A⋅M⋅ADP⋅Pi ⇌ A⋅M⋅ADP. Filaments were permitted to slide relative to one another to maintain a uniform tension in the fiber, but the ends of the fiber were held fixed. T1 is the tension immediately after the step, before any power-stroke transitions have taken place. T2 is the tension attained once the power-stroke transition of all of the bound heads has been reequilibrated.