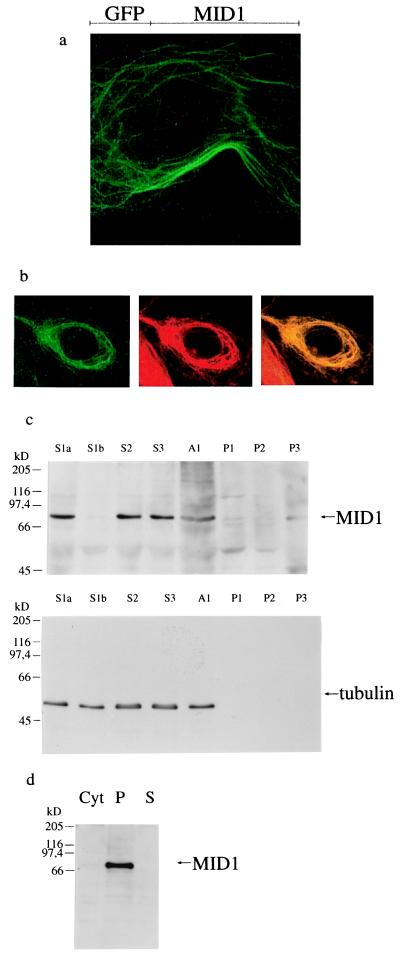
Figure 1.
Subcellular localization of MID1. (a) Filamentous structures revealed by transfection of COS-7 cells with the C-terminal GFP-MID1 fusion protein. (b) Colocalization of the GFP-MID1 fusion protein with microtubules in COS-7 cells. Overlap of the green fluorescent signal of GFP-MID1 and the red staining of the anti-tubulin antibody yield yellow filaments, whereas the neighboring cell without GFP-MID1 expression retains the red of the tubulin staining. (c) Western blot analysis of the subcellular fractions prepared from primary embryonic fibroblasts. MID1 and tubulin are detected in the low- (S1a and S1b), medium- (S2), and high-speed supernatants (S3). The pellets (P1 low-speed pellet, P2 medium-speed pellet, and P3 high-speed pellet) contain neither MID1 nor tubulin. A1 is an aliquot of the homogenized cells. Pellets were resuspended in 2 ml of detergent-containing buffer. Portions of each fraction (150 μl) were acetone-precipitated and resuspended in 40 μl of SDS loading buffer. On the blot incubated with a specific anti-MID1 antibody (Upper), 20 μl of the resuspended acetone precipitates were loaded in each lane, on the blot incubated with anti-tubulin antibodies (Lower), 4 μl from a 1:10 dilution were loaded on each lane. Additional bands visible in the MID1 blot were caused by the high concentrations of protein loaded and were shown to be nonspecific by competition experiments with antigenic peptide (data not shown). (d) Western blot analysis of sedimented, reassembled HeLa microtubules in the presence of cytosol from primary embryonic fibroblasts. Each lane contains 20 μg of protein sample. Lane 1 contains an aliquot of the cytosol. The microtubule-containing pellet was loaded on lane 2. Lane 3 contains the supernatant after precipitation of the reassembled microtubules. A single band at 72 kDa is detected by incubation of the nitrocellulose blot with affinity-purified anti-MID1 in the microtubule-containing pellet and in the cytosol (very weak because of the low expression level of MID1).