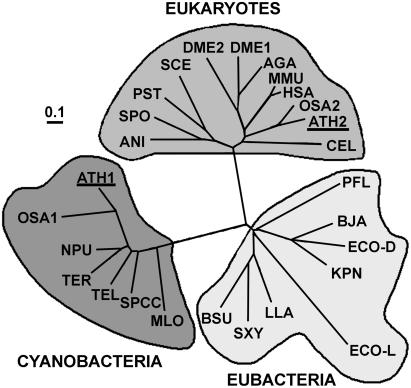
Figure 5.
Phylogenetic tree of xylulose kinases revealing two evolutionary distinct sequence clusters for the Arabidopsis genes. Sequences from Arabidopsis were compared with other annotated xylulose kinases. Alignment was performed with ClustalX. The tree was calculated by neighbor-joining distance method and is represented in an unrooted form. Line lengths indicate the relative distances between nodes. MLO, Mesorhizobium loti (NP_104677); ATH1, Arabidopsis (NP_179732); OSA1, Oryza sativa (NP_912678); TEL, Thermosynechococcus elongatus (NP_682081); SPCC, Synechocystis sp. PPC (NP_442817); NPU, Nostoc punctiforme (NP_488696); TFL, Trichodesmium erythraeum (ZP_00071393); PFL, Pseudomonas fluorescens (ZP_00088158); ECOL, E. coli l-xylulose kinase (NP_418037); ECOD, E. coli xk (AAN32628); KPN, Klebsiella pneumoniae (AAC26499); BJA, Bradyrhizobium japonicum (NP_767759); LLA, Lactococcus lactis (AAD20250); BSU, Bacillus subtilis (NP_389643); SXY, Staphylococcus xylosus (P27155); SPO, Schizosaccharomyces pombe (NP_587930); ANI, Aspergillus niger (CAC83746); SCE, S. cerevisiae (NP_011710); PST, Pichia stipitis (AAF72328); ATH2, Arabidopsis (NP_199776); OSA2, O. sativa (XP_479289); HSA, Homo sapiens (NP_005099); MMU, Mus musculus (AAH25442); DME2, Drosophila melanogaster (NP_608543); AGA, Anopheles gambiae (EAA06371); DME1, D. melanogaster (NP_650582); CEL, Caenorhabditis elegans (NP_498988).