FIG. 10.
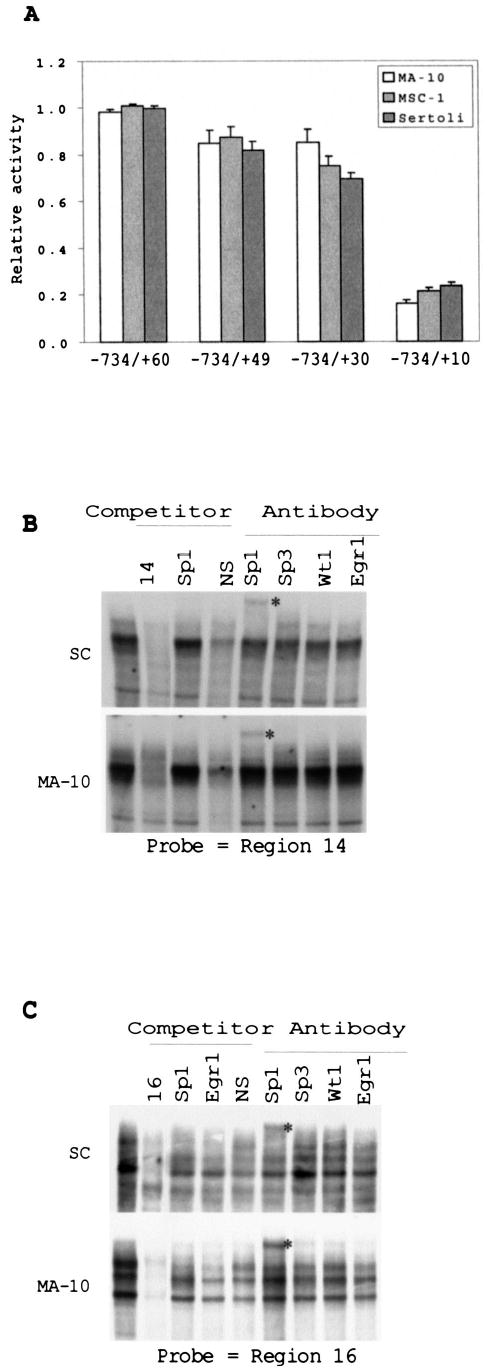
Two downstream GC-rich elements that bind Sp1 in vitro play a role in promoter activity. A) The sequence between positions +30 and +10 is important for promoter activity. Three promoter fragments with increasing deletions 3′ to the transcription start site were introduced into the SF-1 promoter. Promoter activities were analyzed by transient transfection of MA-10, MSC-1, and Sertoli cells, and the activities are expressed relative to the original SF1(−734/+60)Luc construct (see Fig. 4). Error bars represent the SEM. B) EMSAs were conducted using a probe to region 14 and nuclear proteins of either Sertoli or MA-10 cells. Where indicated above the lanes, binding reactions were performed in the presence of a 200-fold excess of competitor oligodeoxynucleotides or antibodies against Sp1, Sp3, Wt1, and Egr1. C) EMSAs were performed as described in A but with a probe to region 16, and competitors for reactions performed with Sertoli cell (SC) extracts were added at 100-fold molar excess. Sequences of the probes and competitors are given in Table 2. The supershifted complexes are denoted by asterisks to the right of the lanes, and the SP1-containing bands are indicated by arrows.
