FIG. 11.
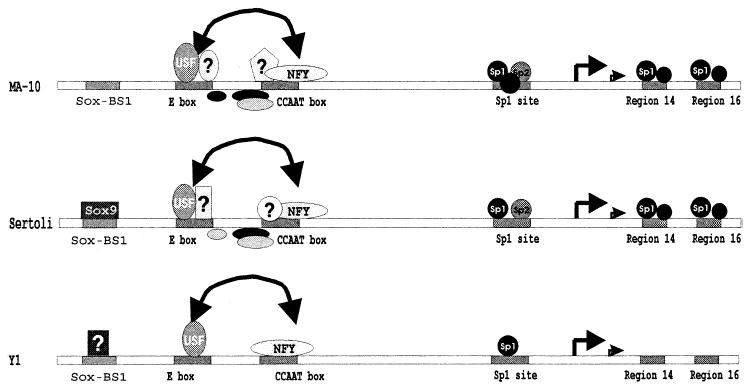
Model for transcriptional regulation of the SF-1 gene. Shown is a schematic representation of the protein complexes that bind the SF-1 proximal promoter between positions −120 and +30 together with their recognition sites in MA-10 (top), Sertoli cells (middle), and Y-1 cells (bottom). Efficient transcription requires input from six cis-acting elements: the Sox-BS1 site, E box, CCAAT box, the Sp1 site, and elements within regions 14 and 16. Interaction between the E box and CCAAT box is indicated by the double-headed arrow. The bent arrows mark the identified transcription start sites (major site at +1). The known factors (Sox9, USF, NF-Y, and Sp proteins) that interact with the proximal promoter in vitro are specified as well as those that have not yet been identified. These include specific complexes that bind the intervening region between the E box and the CCAAT boxes as well as those that bind within these elements. Regulation of SF-1 through binding of Sox9 to the Sox-BS1 site in MA-10 cells remains unclear [41].
