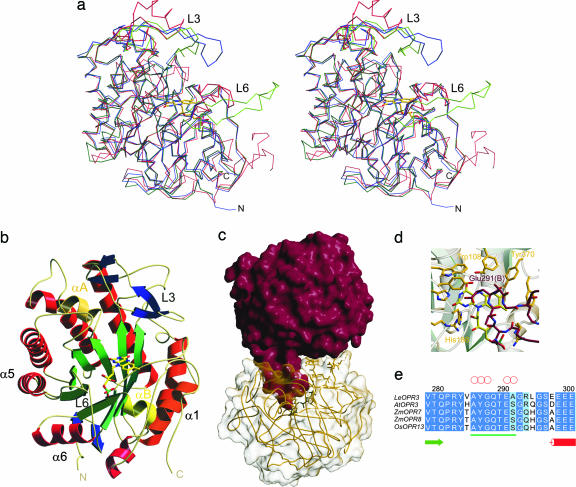
Fig. 2.
Overall structure of OPR3 from L. esculentum. (a) Stereoview representation of the superimposed Cα traces of OPR3 (green), OPR1 (blue), and OYE (red). (b) Ribbon representation of one OPR3 monomer. The FMN cofactor is depicted as a stick model. (c) Overall structure of the OPR3 dimer. The finger-like loop L6 of protomer A (red) is bound into the substrate-binding pocket of protomer B (yellow) and vice versa. (d) Detailed view of the active site of OPR3 (yellow) blocked by amino acids of loop L6 of the partner protomer (red). (e) Multiple sequence alignment of the insertion (underlined in green) in loop L6 of OPR3-like enzymes. Red circles indicate amino acids that form hydrogen bonds to active-site amino acids.