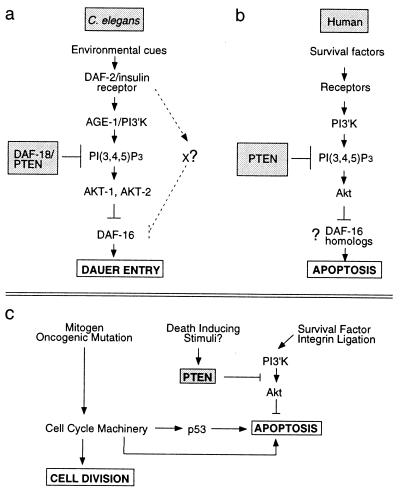
Figure 3.
PI3′K signaling modules in mammals and nematodes have implications for cancer. (a) The C. elegans AGE-1 PI3′K homolog is recruited by the DAF-2 IRL protein. PI3′K generates PtdIns-3,4,5-P3, whereas the DAF-18 PTEN homolog degrades this second messenger. PtdIns-3,4,5-P3 and its derivative PtdIns-3,4-P2 lead to the activation of Akt-family kinases. AKT-1 and AKT-2 may directly phosphorylate the DAF-16 forkhead transcription factor, thereby antagonizing its function (17). DAF-16 forkhead activity leads to induction of the dauer state (18, 19). Loss of DAF-16 activity prevents dauer formation. (b) In mammals, PTEN and PI3′K similarly antagonize one another to regulate local PtdIns-3,4,5-P3 levels and thus Akt activation. Although C. elegans Akt homologs have not been shown to play a role in nematode programmed cell death, mammalian Akt can potently protect cells against apoptosis. DAF-16 homologs (18) of the FKHR family (38) may play a role in the regulation of apoptosis by Akt. (c) PTEN and PI3′K regulate the integration of extracellular survival signals into the normal cell division cycle. Loss of PTEN results in increased Akt activity and increased cell survival even in the presence of the proapoptotic cues induced by aberrant cell division.