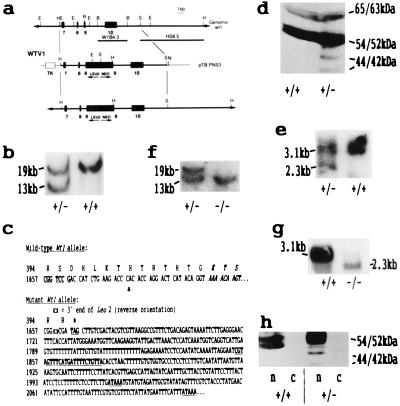
Figure 1.
(a) Strategy for the disruption of exon 9 of the murine Wt1 gene. The ZF domain of the Wt1 locus is indicated, showing exons 7 (ZF1, 151 bp), 8 (ZF2, 90 bp), 9 (ZF3, 84 bp + 9 bp alternative splice, ASII), and 10 (ZF4, 151 bp). The isogenic replacement targeting vector, WTV1, derived from pZNTV3, contained 11-kb homology with the Wt1 gene. The location of the neo (Leu2/neo) and thymidine kinase (TK) expression cassettes, used for positive and negative selection, respectively, are shown. Thick lines, genomic DNA; thin lines, plasmid DNA (pBluescript, Stratagene). The vector was linearized by NotI digestion before electroporation. The two probes used for Southern analysis are indicated: one internal (W1B4.3, a 4.3-kb BamHI fragment) and one external (HS 8.5, a 8.5-kb fragment from an SalI-HindIII double digest) to the homology. Restriction sites: E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; R, RsrII; B, BamHI; S, SalI; N, NotI. (b) Southern blot of DNA (10 μg per lane) from wild-type (+/+) and targeted (+/−) ES cells after restriction with HindIII and hybridization with the external probe HS8.5. An identical pattern was obtained with W1B4.3. Bands corresponding to the wild-type Wt1 allele (19 kb) and the targeted Leu2/neo-containing allele (13 kb) are indicated. (c) Nucleotide sequence and amino acid composition of part of exon 9 of the mutant Wt1 allele determined by sequencing a 262-bp PCR product (derived from WTV1) that spans the RsrII site (CG′GTCCG) in exon 9 into which the Leu2/neo cassette was inserted. The forward primer (DS26393; 5′-TGAAACCATTCCAGTGTAAAAC-3′) was located in exon 9 immediately upstream of the RsrII site, and the reverse primer (DS47495) was located within the Leu2 gene (underlined, bold type). The translational stop signal (TAG) and polyadenylation sites (ATAAA) are indicated. ∗, Translational stop. (d) Western analysis of nuclear proteins (≈50 μg per lane) from wild-type (+/+) and targeted (+/−) ES cells analyzed with the 6F-H2 antibody. In heterozygous cells the wild-type 65-/63-kDa and 54-/52-kDa proteins and mutant 44-/42-kDa (WT1tmT396) proteins (±exon 5) were present in the ratio 4:20:1. (e) Northern blot of total poly(A)+ RNA (≈1 μg per lane) from wild-type (+/+) and targeted (+/−) ES cells hybridized with the Wt1 cDNA probe WT21. The wild-type transcript is 3.1 kb, and the mutant transcript is 2.3 kb, as anticipated (see b). (f) Southern blot of HindIII-digested DNA (10 μg per lane) from ES cells hybridized with the internal probe W1B4.3, showing homozygosity for the Wt1tmT396 mutation (−/−). (g) Northern blot of total poly(A)+ RNA (≈1 μg per lane) from wild-type (+/+) and Wt1tmT396 homozygous ES cells (−/−) hybridized with the Wt1 cDNA probe WT21. (h) Western analysis (≈50 μg per lane) with the 6F-H2 antibody. Equivalent cell numbers of cytoplasmic (c) and nuclear (n) extracts were analyzed from wild-type (+/+) and targeted (+/−) ES cells.