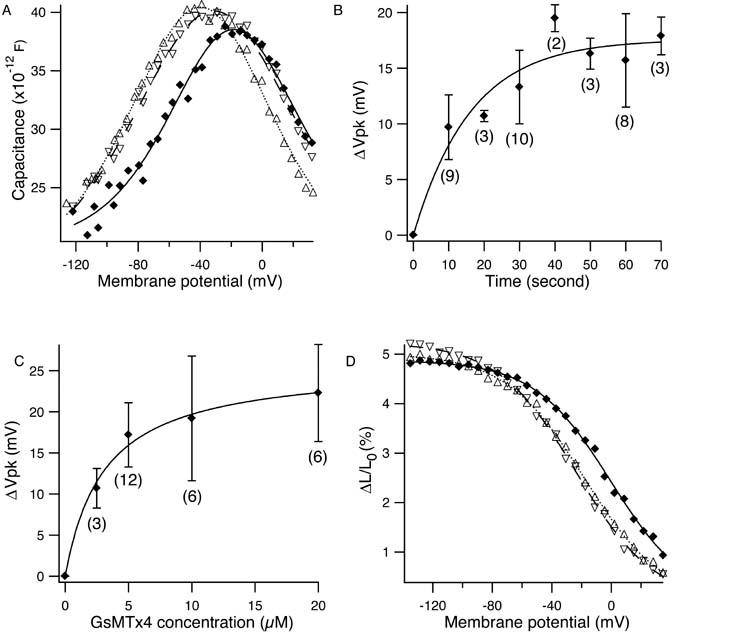
Figure 1.
Effects of GsMTx4 on the outer hair cell motor. (A) Effect on the membrane capacitance. Control (Δ), 5 μM GsMTx4 (♦), and recovery (∇). Parameter values are (mean±SD): for control, q = (0.84±0.04) e (electronic charge), Clin = (17.8 ± 0.1) pF, Vpk = (−39.8 ± 0.4) mV; for 5 μM GsMTx4, q =(0.93±0.05) e, Clin = (20.1±0.1) pF, Vpk = (−18.4±0.8) mV; and for recovery, (0.74 ± 0.04) e, Clin = (17.1 ± 0.1) pF, Vpk = (−31.2 ± 0.5) mV. (B) The time course of voltage shift. The fit with a single exponential gives the time constant of (17.6 ± 1.6) s. (C) Dose response. The curve fit with the mass action law gives the dissociation constant of (3.1±0.6) μM. The maximal shift is (26 ± 1) mV. (D) Effect on voltage dependent axial strain. Control (Δ), 20 μM GsMTx4 (♦), and wash-out (∇). Error bars show standard deviations. The number of data points are shown in the parentheses. The holding potential is −75 mV.