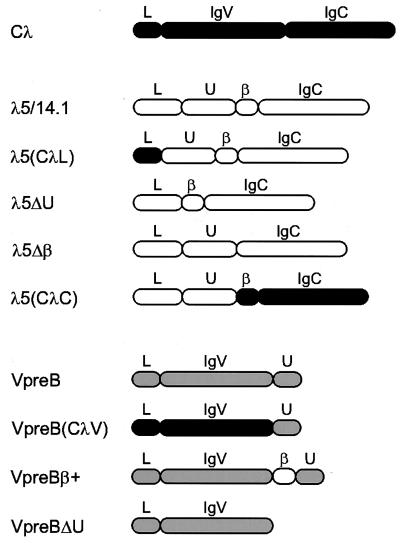
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of wild-type and mutant proteins included in this study. The domain structure of conventional λ light chain (■), λ5/14.1 (□), and VpreB (░⃞) are indicated. Wild-type λ5/14.1 has four cysteines, one in the unique region, two that form the disulfide bridge in the Ig domain and one that is required for binding to the mu heavy chain; VpreB has only two cysteines both of which lie within the Ig-like domain. The λ5(CλL) mutant has the 19-amino acid leader sequence of conventional λ light chain and the169-amino acid mature λ5/14.1 polypeptide. The λ5(CλC) mutant contains the 44-amino acid leader peptide and 50-amino acid unique region of λ5/14.1 and the 119-amino acid Jλ2 and Cλ2 sequence of conventional λ light chain. Mutants λ5ΔU and λ5Δβ lack the 50-amino acid unique region (codon 45–94) and 14-amino acid β strand (codon 95–108), respectively. The VpreB(CλV) contains the leader sequence and variable region of λ light chain (codon 1–114 of Vλ1–13) without the ninth β strand; like VpreB, it does include the 24 amino acids of the unique region of VpreB (codon 122–145 of VpreB). The mutant VpreBβ+ has the 14-amino acid Jλ region from λ5/14.1 (codon 95–108 of λ5/14.1) inserted between the variable region and the unique region of VpreB, completing the nine β-strand Ig variable domain. VpreBΔU lacks carboxyl-terminal 24-amino acid unique region. The domain structure of the wild-type and the mutants are shown as follows: L, leader peptide; U, unique region; IgV, Ig variable domain; IgC, Ig constant domain; β, β strand homologous to Ig J region.