Figure 2.
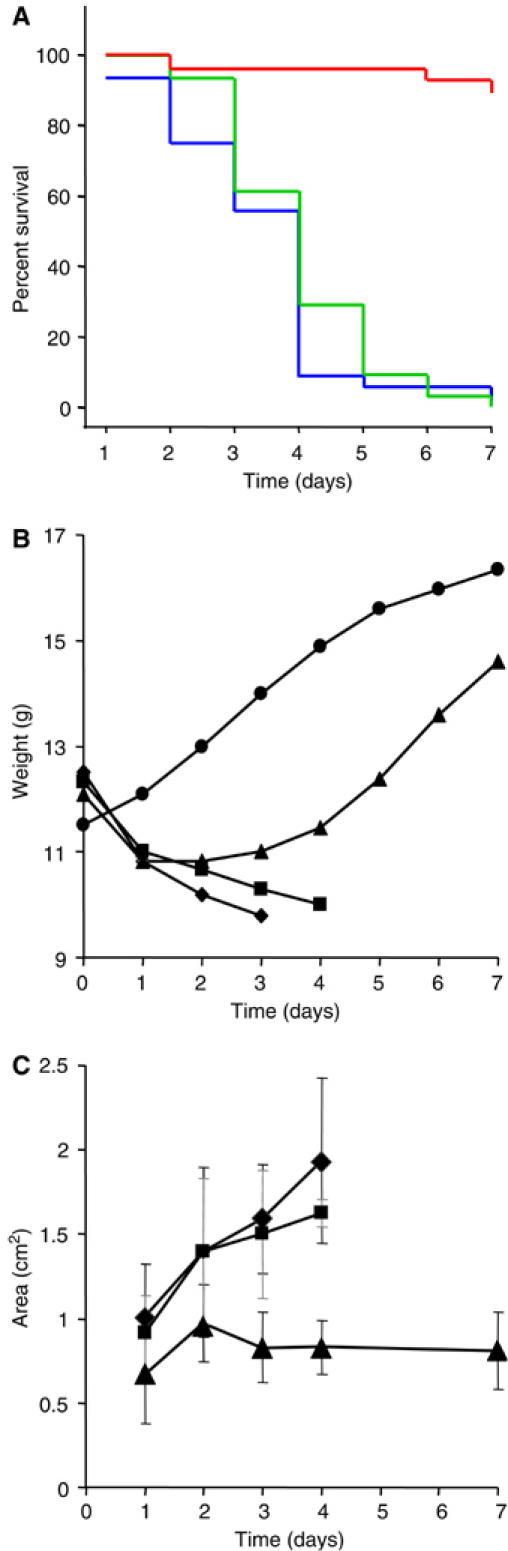
ScpC significantly contributes to virulence in the murine model of GAS necrotizing soft tissue infections. (A) Inactivation of scpC but not of scpA abolished lethality of GAS. Mice were injected subcutaneously with 1 × 108 CFU of WT ( n=32), ΔscpA (
n=32), ΔscpA ( n=31), and ΔscpA/ΔscpC (
n=31), and ΔscpA/ΔscpC ( n=28) and survival was monitored daily. The Kaplan–Meier analysis performed on five different experiments shows P<0.001 for ΔscpA/ΔscpC versus WT or versus ΔscpA and P>0.05 for WT versus ΔscpA (log rank (Mantel–Cox) test). (B) Weight change in control mice (•) and mice challenged with 1 × 108 CFU of WT (♦), ΔscpA (▪), and ΔscpA/ΔscpC (▴). Experiments were repeated five times with similar results. (C) Mean total lesion size (cm2). Mice were injected with 1 × 108 CFU of WT (♦ n=9), ΔscpA (▪ n=15), and ΔscpA/ΔscpC (▴ n=9), photographed daily, and the area was calculated using ImageJ software. Error bars represent s.d. WT and ΔscpA versus ΔscpA/ΔscpC P<0.05 (Student's test) for time points 1 and 2 and P<0.001 (Student's test) for time points 3 and 4. WT versus ΔscpA P>0.05 (Student's test) at all time points.
n=28) and survival was monitored daily. The Kaplan–Meier analysis performed on five different experiments shows P<0.001 for ΔscpA/ΔscpC versus WT or versus ΔscpA and P>0.05 for WT versus ΔscpA (log rank (Mantel–Cox) test). (B) Weight change in control mice (•) and mice challenged with 1 × 108 CFU of WT (♦), ΔscpA (▪), and ΔscpA/ΔscpC (▴). Experiments were repeated five times with similar results. (C) Mean total lesion size (cm2). Mice were injected with 1 × 108 CFU of WT (♦ n=9), ΔscpA (▪ n=15), and ΔscpA/ΔscpC (▴ n=9), photographed daily, and the area was calculated using ImageJ software. Error bars represent s.d. WT and ΔscpA versus ΔscpA/ΔscpC P<0.05 (Student's test) for time points 1 and 2 and P<0.001 (Student's test) for time points 3 and 4. WT versus ΔscpA P>0.05 (Student's test) at all time points.
