Figure 5.
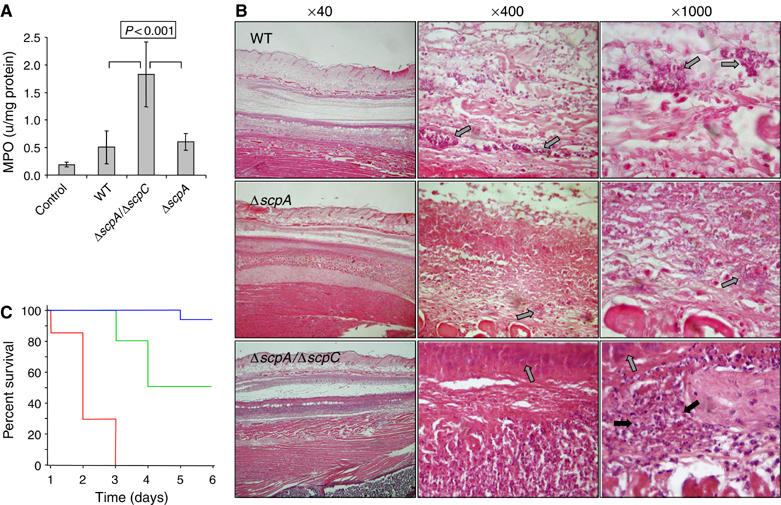
ScpC impairs PMN recruitment. (A) Forty-eight hours after inoculation, lesional (GAS) and control (PBS) 6 mm punch biopsy specimens were taken and the amount of MPO activity (units/mg protein) was determined. Each bar represents the mean±s.d. of two determinations conducted on four specimens. P<0.001 (Student's test) of ΔscpA/ΔscpC versus either WT or ΔscpA. (B) Representative photomicrographs of sections labeled with H&E prepared 2 days after inoculation with WT and its derived mutants. The gray arrow indicates presence of bacteria whereas the black arrow indicates presence of PMN. (C) PMN depletion renders mice sensitive to the ΔscpA/ΔscpC mutant. Mice were injected subcutaneously with 1 × 108 CFU of ΔscpA/ΔscpC and survival was monitored daily in cyclophosphamide-treated ( n=7), RB6-8C5-treated (
n=7), RB6-8C5-treated ( n=10), or PBS-treated (
n=10), or PBS-treated ( n=17) mice. The Kaplan–Meier analysis shows statistically significant difference (P<0.001) in the survival of the three groups of mice (using the log rank (Mantel–Cox) test).
n=17) mice. The Kaplan–Meier analysis shows statistically significant difference (P<0.001) in the survival of the three groups of mice (using the log rank (Mantel–Cox) test).
