Figure 7.
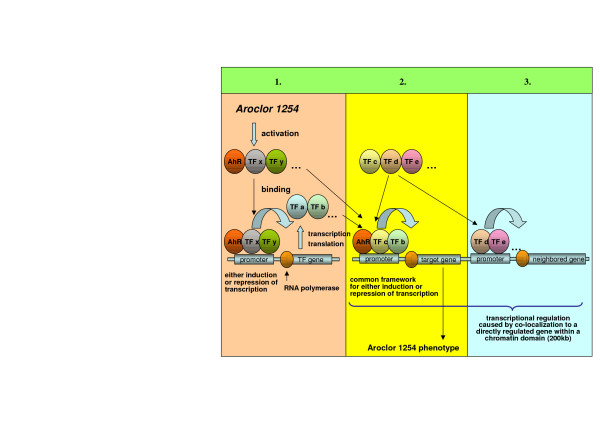
The coordinate events which resulted in gene regulation in response to Aroclor 1254. 1) The Aroclor 1254-activated nuclear transcription factor AhR influences the expression of different transcription factors by binding to AhR recognition sites in corresponding promoters. These transcription factors constitute the basis of a regulatory gene network that again influences the expression of different genes. Other transcription factors could also be primary targets of Aroclor 1254. 2) The Aroclor 1254-activated nuclear transcription factor AhR seems to act in concert with other transcription factors, because a common framework of the corresponding binding sites could be identified proximal to AhR in the Aroclor 1254-regulated gene promoters. The combination of co-acting transcription factors might be one reason for the level of gene expression being either induced or repressed. Other transcription factors whose sites are found in the neighborhood of AhR binding sites could well be primary targets of Aroclor 1254. 3) Chromosomal localization seems to be important in the large-scale regulation of mRNA transcripts in response to Aroclor 1254. Hence, genes in neighborhood of direct Aroclor 1254-induced transcriptional regulation (primary effect), might be co-expressed through the accessibility of their promoters for transcription factors whose transcription was altered by Aroclor 1254 (secondary effect).
