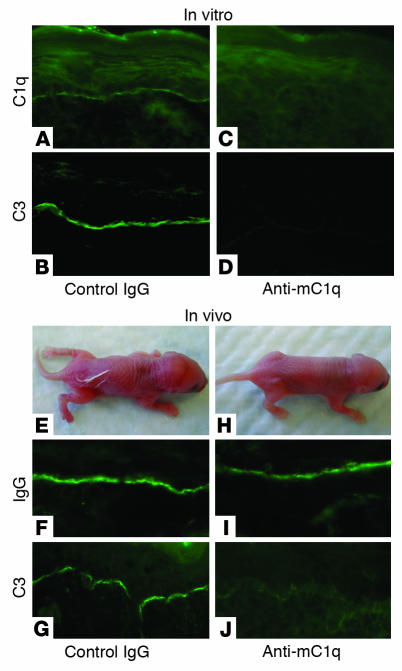
Figure 2. C1q inhibition.
(A–D) In vitro C1q blocking. Neonatal mouse skin sections (5 μm) were incubated with pathogenic anti-mBP180 IgG followed by anti-mC1q or control antibody. Control IgG–treated skin sections showed C1q and C3 staining at BMZ (A and B), while anti-mC1q–treated sections showed no C1q and C3 staining (C and D). (E–J) In vivo C1q blocking. Neonatal WT mice were pretreated with anti-mC1q or isotype control IgG (5 μg/g body weight), injected with pathogenic anti-mBP180 IgG (2.64 mg/g body weight), and examined 12 hours after pathogenic IgG injection. (E) The control IgG–treated mice developed BP disease. (F and G) Direct IF showed deposition of rabbit IgG and mouse C3 at the BMZ. In contrast, mice pretreated with anti-mC1q antibody and injected with the same dose of pathogenic IgG showed no skin lesions (H), and direct IF exhibited the BMZ deposition of rabbit IgG (I) but not mouse C3 (J). Three independent experiments were performed per group. Magnification, ×200 (A–D, F, G, I, and J).