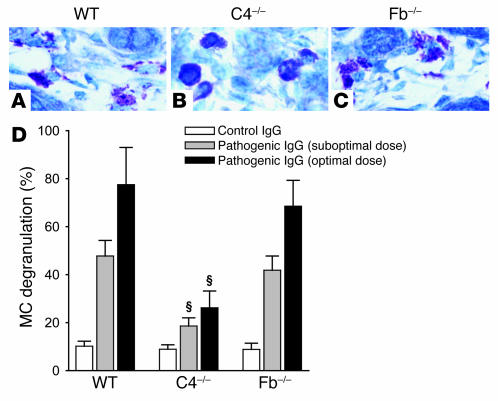
Figure 4. MC degranulation is impaired in C4–/– mice injected with pathogenic IgG.
WT, C4–/–, and Fb–/– mice were injected with an optimal or suboptimal dose (2.64 or 2.0 mg/g body weight, respectively) of pathogenic anti-mBP180 IgG or with control IgG (2.64 mg/g body weight) and examined for MC degranulation 2 hours after IgG injection (peak of MC degranulation; n = 12 per group). (A–C) Toluidine blue staining. WT (A) and Fb–/– (C) mice showed extensive MC degranulation in toluidine blue–stained skin sections. In contrast, C4–/– mice (B) exhibited much less MC degranulation. Original magnification, ×400. (D) Quantification of MC degranulation. MCs in the dermis of the IgG-injected skin biopsies were counted and classified as degranulated or normal (see Methods). Total MCs in 5 random fields were counted (mean, 34.58 ± 9.29), and percent MC degranulation was calculated as described in Methods. MC degranulation was significantly reduced in C4–/– mice at both suboptimal and optimal doses of pathogenic IgG compared with WT. There was no difference in MC degranulation between WT and Fb–/– mice at suboptimal (P = 0.054) or optimal doses (P = 0.073). Three independent experiments were performed per group. ΧP < 0.001 versus WT at the respective time points.