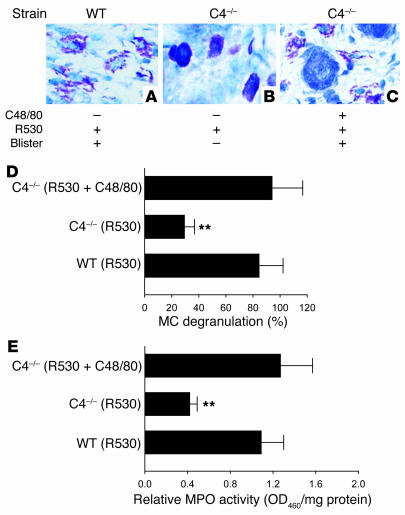
Figure 6. Effect of MC degranulating agent on PMN infiltration and subepidermal blistering in pathogenic IgG–injected C4–/– mice.
WT and C4–/– mice were injected with pathogenic anti-mBP180 R530 IgG (2.6 mg/g body weight) with or without pretreatment of the MC degranulating agent compound 48/80 (C48/80) and were examined 2 hours (for toluidine blue staining) and 12 hours (for clinical examination and MPO assay) after IgG injection. (A–C) Clinical examination and toluidine blue staining of the mouse skin showed subepidermal blisters and MC degranulation in WT (A) and C4–/– mice with compound 48/80 pretreatment (C). (B) In contrast, C4–/– mice without compound 48/80 treatment exhibited no skin lesions and minimal MC degranulation. (D) MCs in the dermis of the skin were counted and classified as degranulated or normal. Total MCs in 5 random fields were counted (mean, 31.72 ± 8.41), and percent MC degranulation was calculated. As expected, MC degranulation was significantly reduced in C4–/– mice compared with WT mice. However, a significant increase of MC degranulation was seen in the skin of compound 48/80–treated C4–/– mice. n = 6 per group. (E) MPO activity assay revealed significantly higher levels of PMN infiltration in WT and C4–/– mice with compound 48/80 pretreatment than those without it. Tissue MPO activity at the injection sites was expressed as relative MPO activity. Three independent experiments were performed per group. n = 6 per group. **P < 0.01 versus WT and pretreated C4–/– mice.