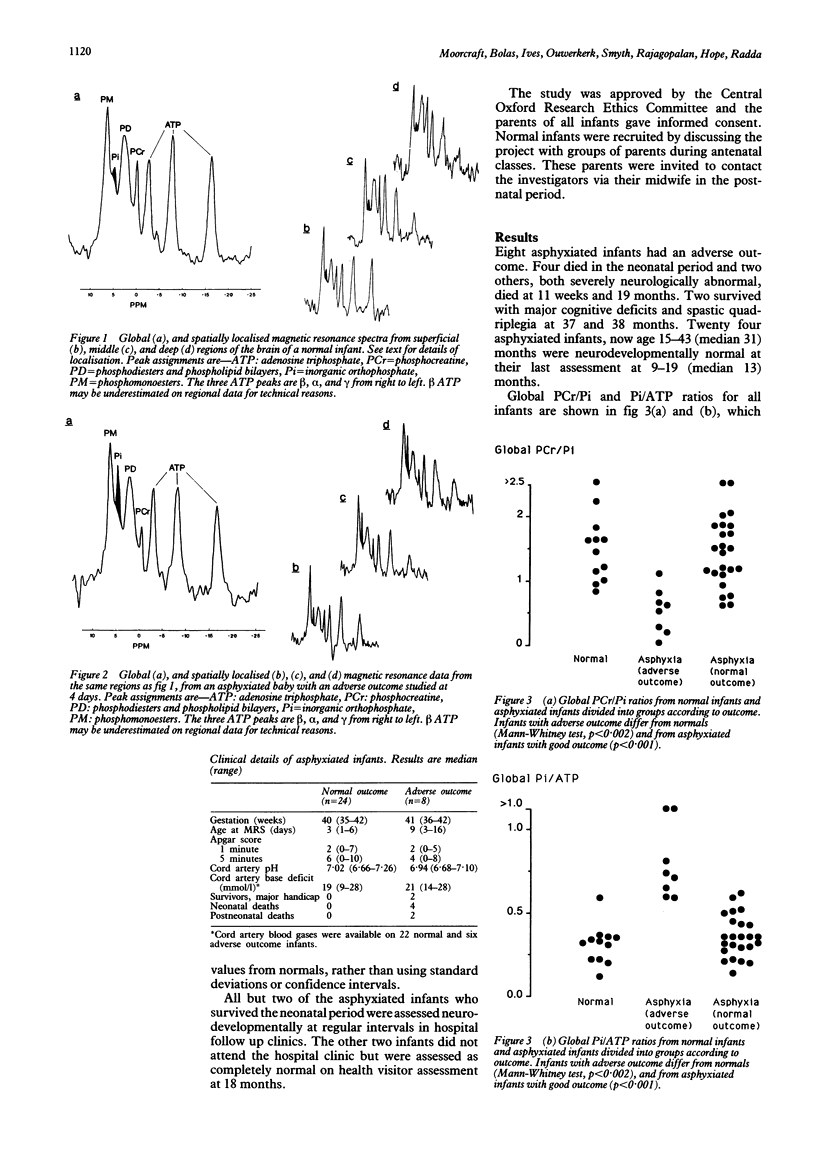
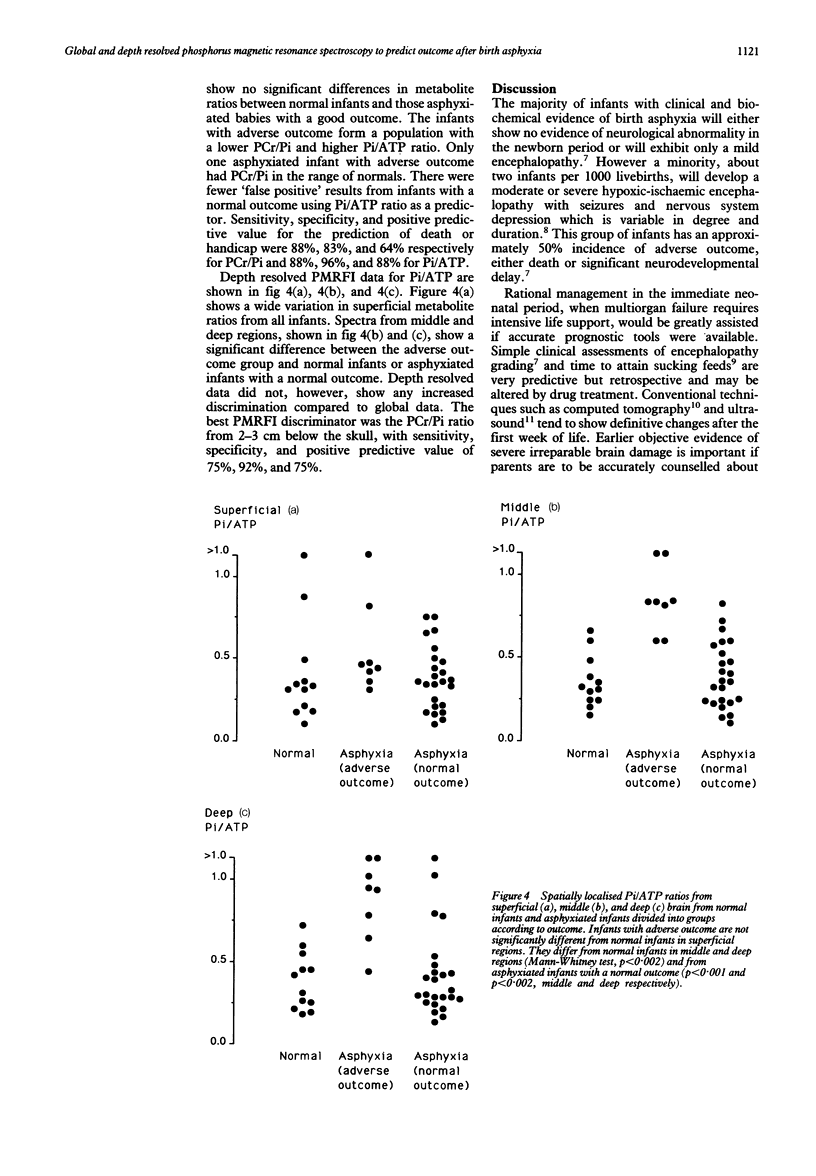
Abstract
Twelve normal and 32 asphyxiated neonates were studied using global and depth resolved phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy (31PMRS). Eight of the asphyxiated group died or survived with major neurodevelopmental abnormalities. A global phosphocreatinine/inorganic phosphate (PCr/Pi) ratio below the range of values from normal infants predicted adverse outcome after asphyxia with a positive predictive value of 64%, sensitivity 88%, and specificity 83%. Corresponding values for global inorganic orthophosphate/adenosine triphosphate (Pi/ATP) ratios were positive predictive value 88%, sensitivity 96%, and specificity 88%. Spatially localised MRS data, obtained using phase modulated rotating frame imaging, showed cerebral energy metabolism to be more abnormal in deep than superficial regions after birth asphyxia. However, in this population of full term infants none of the regional metabolite concentrations were superior to global data for prediction of outcome.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer L. N., Levene M. I., Evans D. H. Cerebral artery Doppler ultrasonography for prediction of outcome after perinatal asphyxia. Lancet. 1986 Nov 15;2(8516):1116–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azzopardi D., Wyatt J. S., Cady E. B., Delpy D. T., Baudin J., Stewart A. L., Hope P. L., Hamilton P. A., Reynolds E. O. Prognosis of newborn infants with hypoxic-ischemic brain injury assessed by phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr Res. 1989 May;25(5):445–451. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198905000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock D. S., Ball W., Jr Postasphyxial encephalopathy in full-term infants: ultrasound diagnosis. Radiology. 1983 Aug;148(2):417–423. doi: 10.1148/radiology.148.2.6867334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackledge M. J., Rajagopalan B., Oberhaensli R. D., Bolas N. M., Styles P., Radda G. K. Quantitative studies of human cardiac metabolism by 31P rotating-frame NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4283–4287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis P. D., Matthews T. G., Clarke T. A., Darling M., Crowley P., Griffin E., O'Connell P., Gorman W., O'Brien N., O'Herlihy C. Neonatal seizures: the Dublin Collaborative Study. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Sep;63(9):1065–1068. doi: 10.1136/adc.63.9.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope P. L., Costello A. M., Cady E. B., Delpy D. T., Tofts P. S., Chu A., Hamilton P. A., Reynolds E. O., Wilkie D. R. Cerebral energy metabolism studied with phosphorus NMR spectroscopy in normal and birth-asphyxiated infants. Lancet. 1984 Aug 18;2(8399):366–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp-Zwahlen A. E., Deonna T., Micheli J. L., Calame A., Chrzanowski R., Cêtre E. Prognostic value of neonatal CT scans in asphyxiated term babies: low density score compared with neonatal neurological signs. Neuropediatrics. 1985 Nov;16(4):209–217. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorcraft J., Bolas N. M., Ives N. K., Sutton P., Blackledge M. J., Rajagopalan B., Hope P. L., Radda G. K. Spatially localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brains of normal and asphyxiated newborns. Pediatrics. 1991 Mar;87(3):273–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnat H. B., Sarnat M. S. Neonatal encephalopathy following fetal distress. A clinical and electroencephalographic study. Arch Neurol. 1976 Oct;33(10):696–705. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500100030012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. S., Edwards A. D., Azzopardi D., Reynolds E. O. Magnetic resonance and near infrared spectroscopy for investigation of perinatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Jul;64(7 Spec No):953–963. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.7_spec_no.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


