Abstract
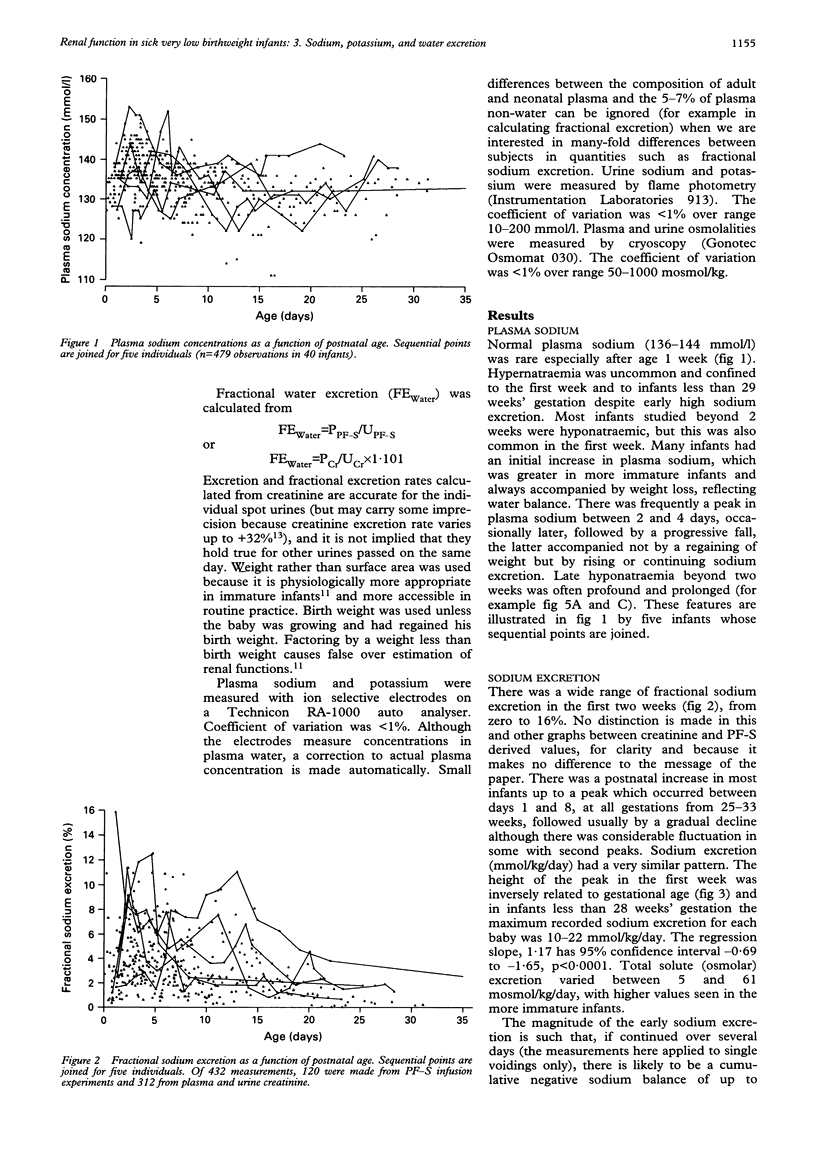
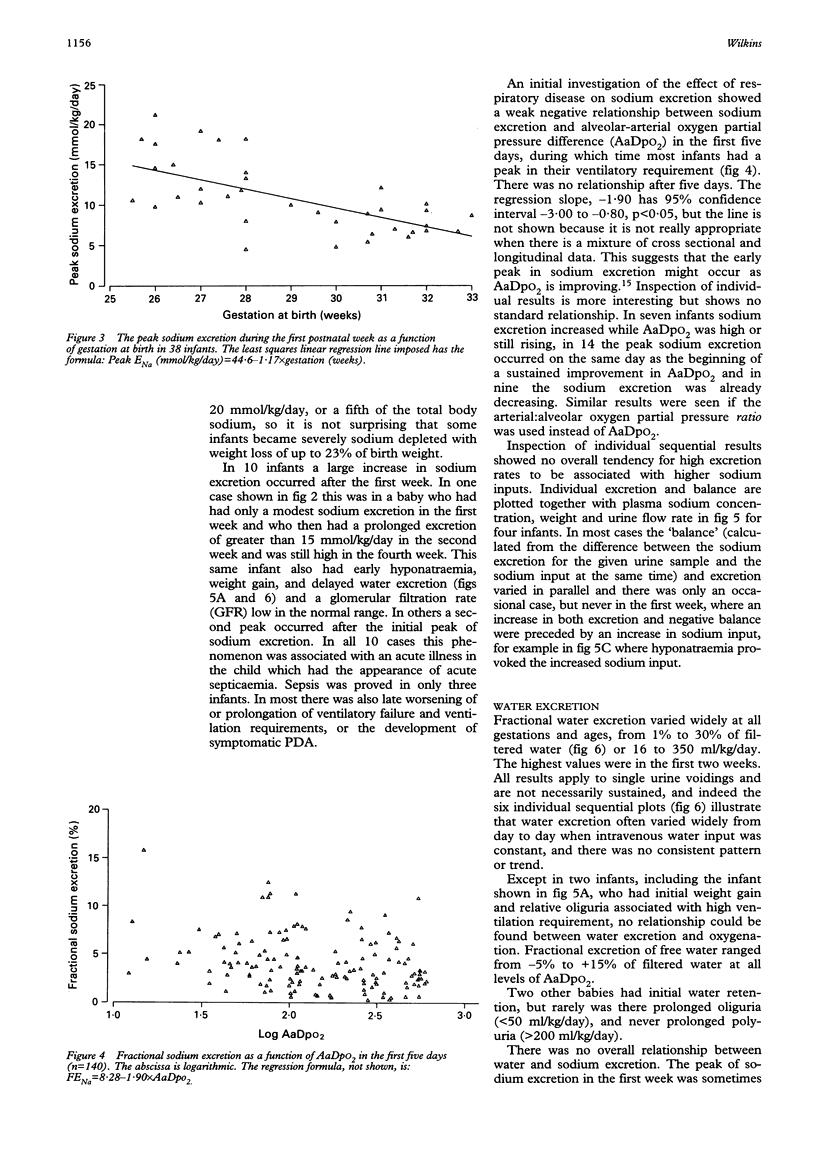
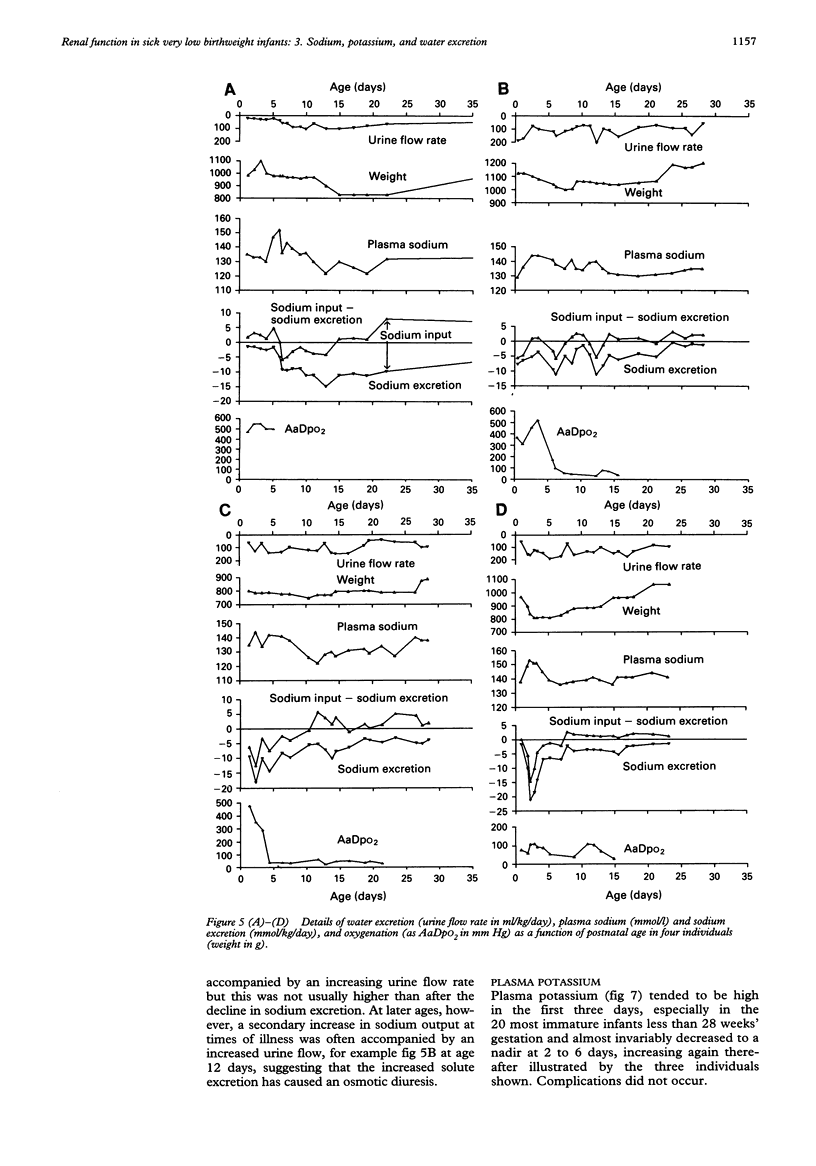
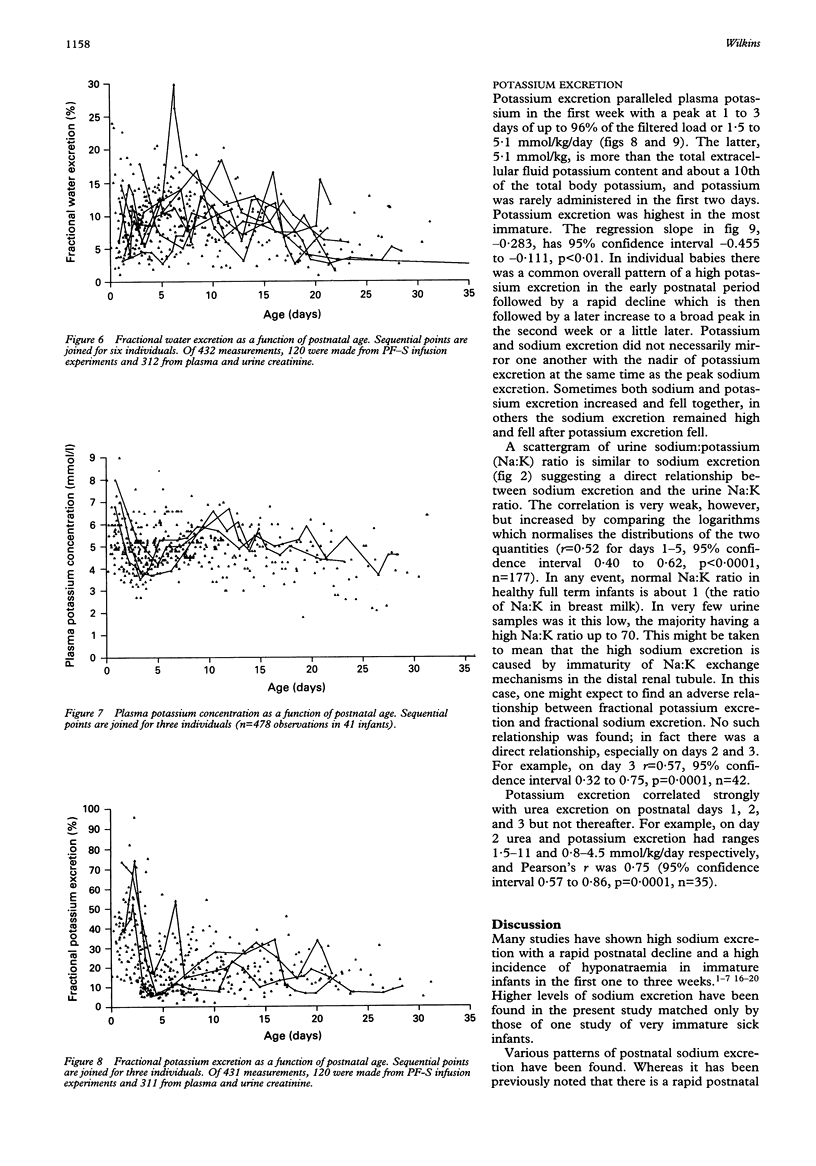
Renal excretion of sodium, water, and potassium was measured on 434 occasions in a sample of 40 infants of 25.5-33 weeks' gestation, birth weight 720-2000 g, between the ages of 0.5 and 36 days. Water excretion varied between 1% and 30% of the glomerular filtration rate, or 15-350 ml/kg/day, and varied widely from day to day in individual infants. Nearly all infants became hyponatraemic before or after the first postnatal week. There were a few instances of hypernatraemia in the first week caused by high insensible water loss. There were high levels of sodium excretion up to 16% of filtered sodium, or 21 mmol/kg/day, in the first two postnatal weeks. Highest levels of sodium excretion were seen in the most immature infants in the first week. In most infants sodium excretion increased either in the first week or later before a subsequent decline. Potassium excretion was often high in the first week, as much as 96% of filtered potassium, or 5 mmol/kg/day, and is associated with early hyperkalaemia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken C. G., Sherwood R. A., Kenney I. J., Furnell M., Lenney W. Mineral balance studies in sick preterm intravenously fed infants during the first week after birth. A guide to fluid therapy. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1989;355:1–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1989.tb11232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dahhan J., Haycock G. B., Chantler C., Stimmler L. Sodium homeostasis in term and preterm neonates. I. Renal aspects. Arch Dis Child. 1983 May;58(5):335–342. doi: 10.1136/adc.58.5.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Dahhan J., Haycock G. B., Nichol B., Chantler C., Stimmler L. Sodium homeostasis in term and preterm neonates. III. Effect of salt supplementation. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Oct;59(10):945–950. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.10.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Broberger O., Herin P., Zetterström R. Salt content in human breast milk during the three first weeks after delivery. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 May;68(3):441–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb05034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Broberger O., Herin P., Zetterström R. Sodium excretion in relation to sodium intake and aldosterone excretion in newborn pre-term and full-term infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Nov;68(6):813–817. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb08217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aperia A., Larsson L., Zetterström R. Hormonal induction of Na-K-ATPase in developing proximal tubular cells. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F356–F360. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arant B. S., Jr Distal tubular sodium handling in human neonates: clearance studies. Contrib Nephrol. 1988;67:130–137. doi: 10.1159/000415389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arant B. S., Jr Fluid therapy in the neonate--concepts in transition. J Pediatr. 1982 Sep;101(3):387–389. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arant B. S., Jr Nonrenal factors influencing renal function during the perinatal period. Clin Perinatol. 1981 Jun;8(2):225–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K., Bovermann G., Roithmaier A., Götz M., Pröiss A., Versmold H. T. Body composition, nutrition, and fluid balance during the first two weeks of life in preterm neonates weighing less than 1500 grams. J Pediatr. 1991 Apr;118(4 Pt 1):615–620. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)83390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierd T. M., Kattwinkel J., Chevalier R. L., Rheuban K. S., Smith D. J., Teague W. G., Carey R. M., Linden J. Interrelationship of atrial natriuretic peptide, atrial volume, and renal function in premature infants. J Pediatr. 1990 May;116(5):753–759. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82667-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brion L. P., Schwartz G. J., Campbell D., Fleischman A. R. Early hyperkalaemia in very low birthweight infants in the absence of oliguria. Arch Dis Child. 1989 Feb;64(2):270–272. doi: 10.1136/adc.64.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chessex P., Reichman B., Verellen G., Putet G., Smith J. M., Heim T., Swyer P. R. Quality of growth in premature infants fed their own mothers' milk. J Pediatr. 1983 Jan;102(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80303-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulthard M. G., Hey E. N. Effect of varying water intake on renal function in healthy preterm babies. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Jul;60(7):614–620. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.7.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad H., Kero P., Takala J., Korvenranta H., Välimäki I. Water, sodium and acid-base balance in premature infants: therapeutical aspects. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 Jan;76(1):47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke S. C., Shah B. L., Vasan U., Raye J. R. Sodium balance in very low-birth-weight infants. J Pediatr. 1978 Nov;93(5):837–841. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)81097-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engle W. D., Arant B. S., Jr Urinary potassium excretion in the critically ill neonate. Pediatrics. 1984 Aug;74(2):259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda Y., Larsson S., Celsi G., Lechene C., Aperia A. Use of experimental models to study the development of renal function. Biol Neonate. 1988;53(4):197–200. doi: 10.1159/000242791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. J. Growth and biochemical response of preterm infants fed human milk or modified infant formula. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 3;308(5):237–241. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302033080501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruskay J., Costarino A. T., Polin R. A., Baumgart S. Nonoliguric hyperkalemia in the premature infant weighing less than 1000 grams. J Pediatr. 1988 Aug;113(2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80288-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guignard J. P., Torrado A., Mazouni S. M., Gautier E. Renal function in respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1976 May;88(5):845–850. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(76)81129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haycock G. B., Aperia A. Salt and the newborn kidney. Pediatr Nephrol. 1991 Jan;5(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00852850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaf D. P., Belik J., Spitzer A. R., Gewitz M. H., Fox W. W. Changes in pulmonary function during the diuretic phase of respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1982 Jul;101(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honour J. W., Valman H. B., Shackleton H. L. Aldosterone and sodium HOMEOSTASIS in preterm infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1977 Jan;66(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1977.tb07815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judd B. A., Haycock G. B., Dalton N., Chantler C. Hyponatraemia in premature babies and following surgery in older children. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 May;76(3):385–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima T., Hirata Y., Fukuda Y., Iwase S., Kobayashi Y. Plasma atrial natriuretic peptide and spontaneous diuresis in sick neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Jul;62(7):667–670. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.7.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson L., Horster M. Ultrastructure and net fluid transport in isolated perfused developing proximal tubules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Feb;54(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80156-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson S. H., Rane S., Fukuda Y., Aperia A., Lechene C. Changes in Na influx precede post-natal increase in Na, K-ATPase activity in rat renal proximal tubular cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1990 Jan;138(1):99–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1990.tb08819.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi N., Hutton J. L. The influence of postnatal respiratory adaptation on sodium handling in preterm neonates. Early Hum Dev. 1990 Jan;21(1):11–20. doi: 10.1016/0378-3782(90)90106-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L., Brook C. G., Shaw J. C., Forsling M. L. Hyponatraemia in the first week of life in preterm infants. Part I. Arginine vasopressin secretion. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):414–422. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees L., Shaw J. C., Brook C. G., Forsling M. L. Hyponatraemia in the first week of life in preterm infants. Part II. Sodium and water balance. Arch Dis Child. 1984 May;59(5):423–429. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.5.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Soriano J., Vallo A., Oliveros R., Castillo G. Renal handling of sodium in premature and full-term neonates: a study using clearance methods during water diuresis. Pediatr Res. 1983 Dec;17(12):1013–1016. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198312000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross B., Cowett R. M., Oh W. Renal functions of low birth weight infants during the first two months of life. Pediatr Res. 1977 Nov;11(11):1162–1164. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197711000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schanler R. J., Oh W. Composition of breast milk obtained from mothers of premature infants as compared to breast milk obtained from donors. J Pediatr. 1980 Apr;96(4):679–681. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80738-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt U., Horster M. Na-K-activated ATPase: activity maturation in rabbit nephron segments dissected in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1977 Jul;233(1):F55–F60. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1977.233.1.F55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Evan A. P. Development of solute transport in rabbit proximal tubule. III. Na-K-ATPase activity. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F845–F852. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer S. G., Bradt S. K., Hall R. T. Postnatal changes in total body water and extracellular volume in the preterm infant with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986 Sep;109(3):509–514. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer S. G., Geer P. G., Goetz K. L. Elevated atrial natriuretic factor in neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1986 Dec;109(6):1028–1033. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortland D., Trounce J. Q., Levene M. I. Hyperkalaemia, cardiac arrhythmias, and cerebral lesions in high risk neonates. Arch Dis Child. 1987 Nov;62(11):1139–1143. doi: 10.1136/adc.62.11.1139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. R., Fisher D. A., Oh W. Renal function and serum aldosterone levels in infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1973 Nov;83(5):854–858. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. R., Oh W. Renal function as a marker of human fetal maturation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1976 Jul;65(4):481–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1976.tb04917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulyok E., Németh M., Tényi I., Csaba I. F., Varga L., Varga F. Relationship between the postnatal development of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and the electrolyte and acid-base status in the sodium chloride supplemented premature infant. Acta Paediatr Acad Sci Hung. 1981;22(1-2):109–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulyok E., Varga F., Györy E., Jobst K., Csaba I. F. On the mechanisms of renal sodium handling in newborn infants. Biol Neonate. 1980;37(1-2):75–79. doi: 10.1159/000241258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulassay T., Rascher W., Seyberth H. W., Lang R. E., Tóth M., Sulyok E. Role of atrial natriuretic peptide in sodium homeostasis in premature infants. J Pediatr. 1986 Dec;109(6):1023–1027. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80293-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulassay T., Seri I., Rascher W. Atrial natriuretic peptide and extracellular volume contraction after birth. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1987 May;76(3):444–446. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1987.tb10496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins B. H. A reappraisal of the measurement of glomerular filtration rate in pre-term infants. Pediatr Nephrol. 1992 Jul;6(4):323–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00869724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins B. H. Renal function in sick very low birthweight infants: 1. Glomerular filtration rate. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Oct;67(10 Spec No):1140–1145. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins B. H. Renal function in sick very low birthweight infants: 2. Urea and creatinine excretion. Arch Dis Child. 1992 Oct;67(10 Spec No):1146–1153. doi: 10.1136/adc.67.10_spec_no.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


