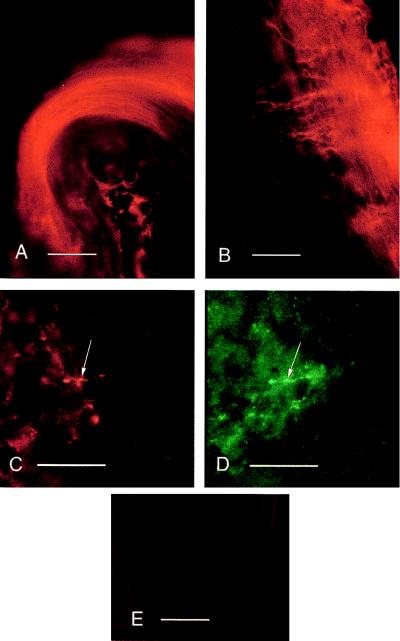
Figure 3.
Immunohistochemistry of HSV-1 vector-mediated expression of human preproenkephalin in mouse dorsal roots and spinal cord. (A) Human proenkephalin (PE-24) immunoreactivity in dorsal root axons of a left dorsal rootlet visualized with Texas Red. Dorsal is down, medial (toward cord) is to the right. (Bar = 100 μm.) (B) Human proenkephalin immunofluorescence in primary afferent axons at the dorsal root entry zone of the dorsal horn ipsilateral to the original infection. Dorsal is up, medial is to the left, and the edge of spinal cord is to the right. (Bar = 100 μm.) (C) Human proenkephalin immunofluorescence in primary afferent terminals (arrow) in the inner substantial gelatinosa. Dorsal is up, and medial is to the right. (Bar = 20 μm.) (D) Met-enkephalin immunoreactivity in the same afferent terminals as in C (arrow) visualized with fluorescein. Area is chosen for relative paucity of Met-enkephalinergic terminals. (Bar = 20 μm.) (E) Lack of human proenkephalin (PE-24) immunoreactivity in dorsal horn at right dorsal root entry zone contralateral to the original infection visualized with Texas Red. Dorsal is up, and the outside of the cord is to the right. (Bar = 100 μm.)